The hosts file lets you control and customize how your computer resolves domain names. Also, it is the first place Windows checks when connecting to a website. The best part is that you can block access to specific websites by editing the hosts file manually. In this article, we’ll walk you through the simple steps to locate and edit hosts file on Windows.
We recommend creating a copy of your hosts file to ensure you can return to the previous working state if something goes wrong. You can also create a restore point to create an extra layer of security. Before we go into more details, let’s find out what the hosts file is on Windows.
What Is a Hosts File on Windows
The hosts file is a local text file that maps hostnames to their corresponding IP addresses. This mapping allows you to override the default Domain Name System (DNS) settings for specific domains, enabling you to achieve various purposes like blocking unwanted websites, testing website changes before deploying them publicly, or redirecting websites to different IP addresses.
Normally, when your computer tries to access a website, it first checks the hosts file. If the hostname and its corresponding IP address are present, your computer directly connects to the website using that address. This bypasses the default DNS lookup process, which involves checking the DNS cache and contacting a DNS server if the address isn’t found in the cache.
However, if the hostname isn’t in the hosts file, your computer continues with the standard DNS lookup process. It checks the DNS cache, and if the address isn’t there, it contacts a DNS server to retrieve the IP address of the website’s server.
Let’s say you’re trying to open GuidingTech’s website. Your computer will directly connect to the website if you’ve previously added GuidingTech’s hostname and its IP address to your hosts file. It won’t waste time searching the DNS cache or contacting a DNS server.
However, if you haven’t added GuidingTech’s information to your hosts file, your computer will follow the standard DNS lookup process as described above.
Where Is the Hosts File Located in Windows
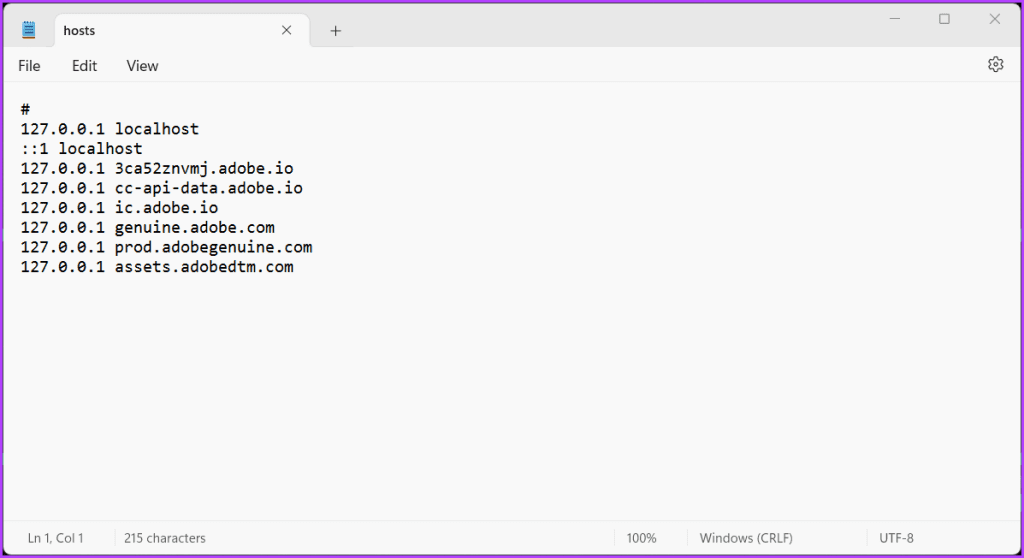
The host files are stored locally on your computer within the C drive. Below is the path to your hosts file:
Step 1: Press the Windows + S key on your keyboard. Type This PC and click Open.
Step 2: Double-click on Local Disk C.
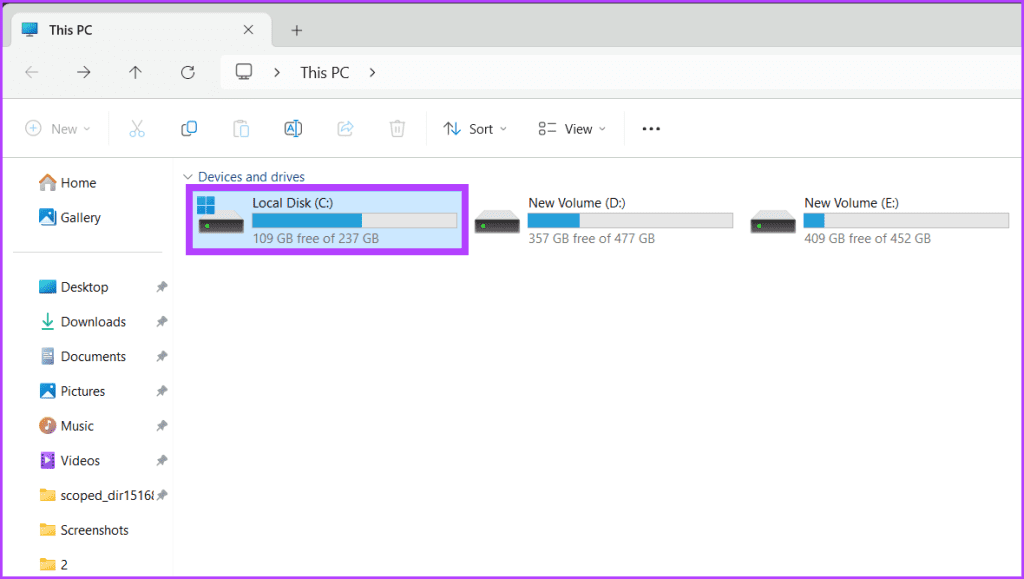
Step 3: Navigate to the Windows folder.
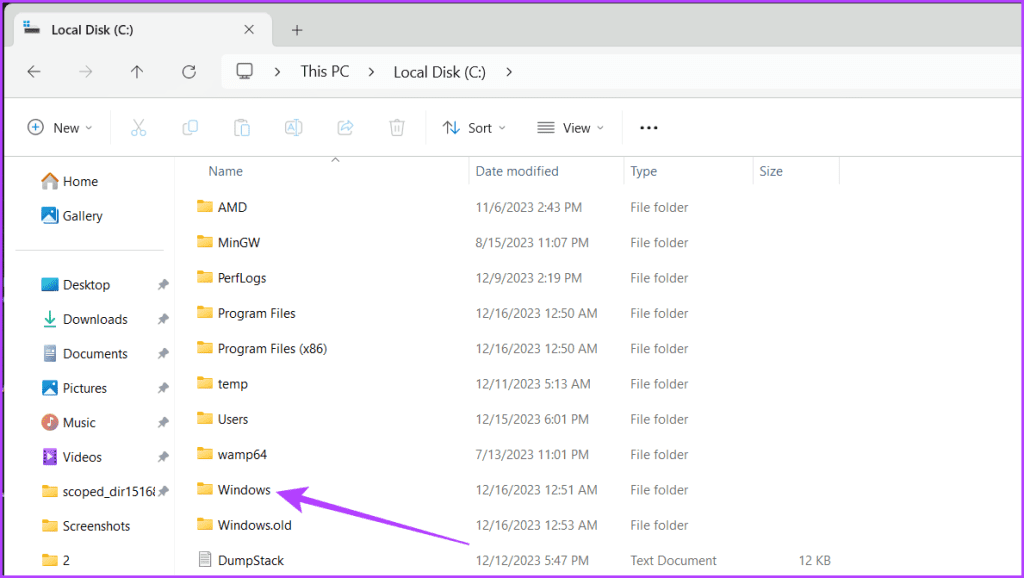
Step 4: Scroll down and open the System32 folder.

Step 5: Search for the drivers folder and open it.
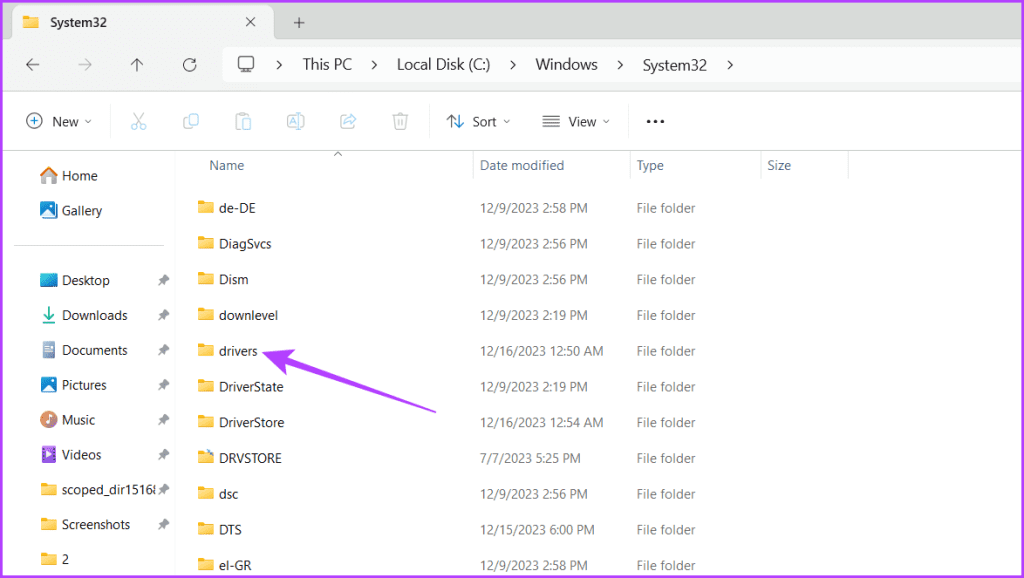
Step 6: Double-click on the etc folder.
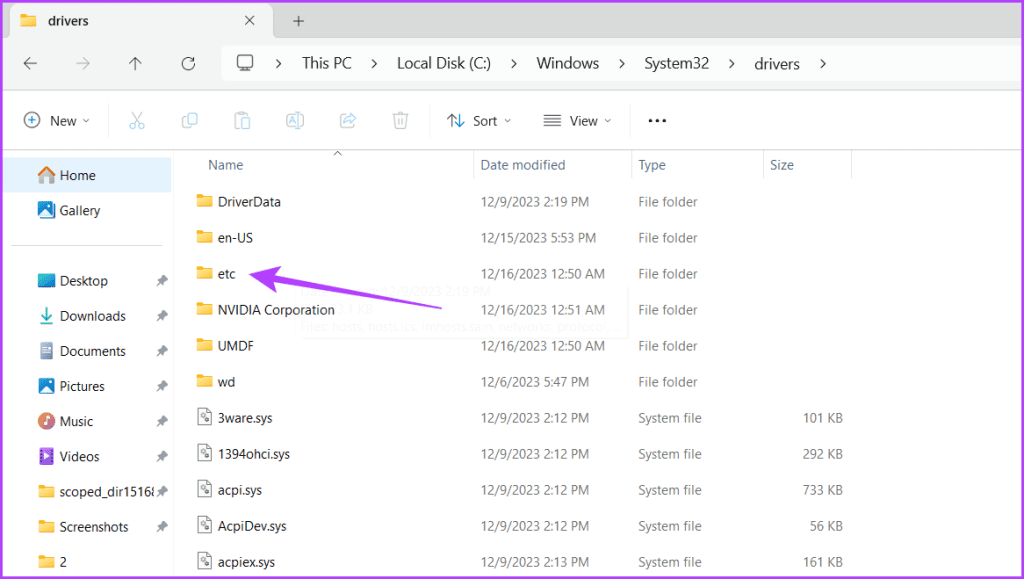
Step 7: Now, you can see your hosts files.
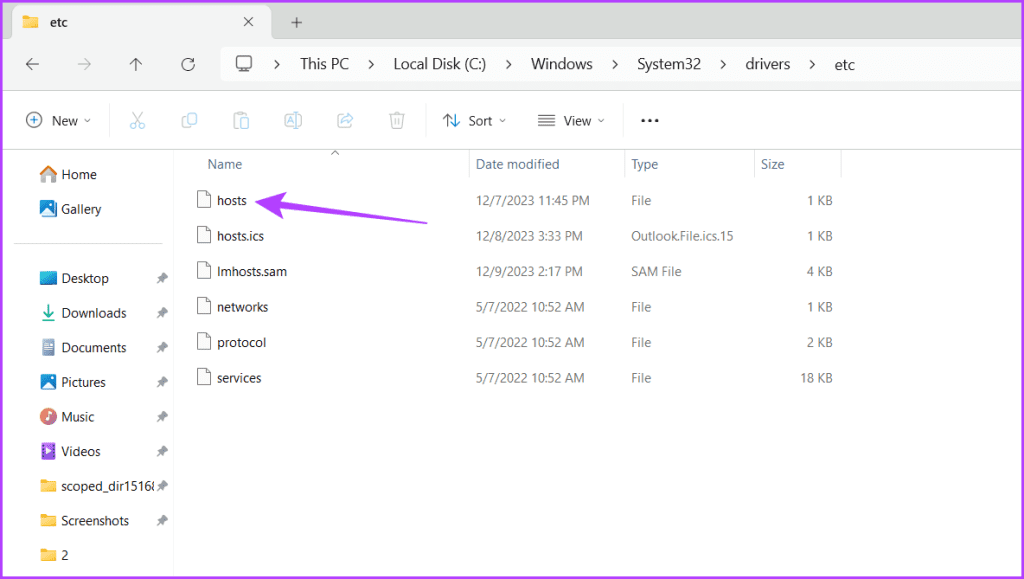
Alternatively, you can also open This PC and paste the following in the address bar:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
How to Edit Hosts File in Windows
Editing the hosts file in Windows is a straightforward process. To get started, you’ll need a text editor, and Windows conveniently includes Notepad as the default option.
However, if you prefer using other text editing tools, you can explore Notepad alternatives. To modify the hosts file, follow these steps:
Step 1: Click the Windows icon and select the search box. Enter Notepad and click Run as administrator. Select Yes when prompted.
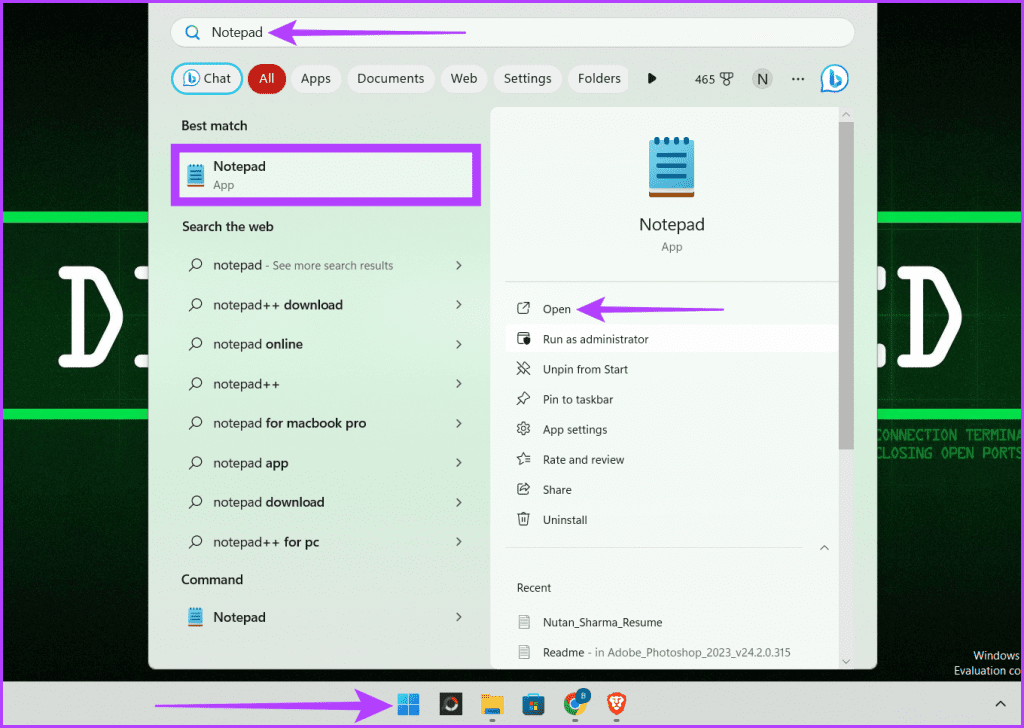
Step 2: Click File and choose Open from the drop-down menu.
Tip: You can also press Ctrl + O to launch the Open menu directly.
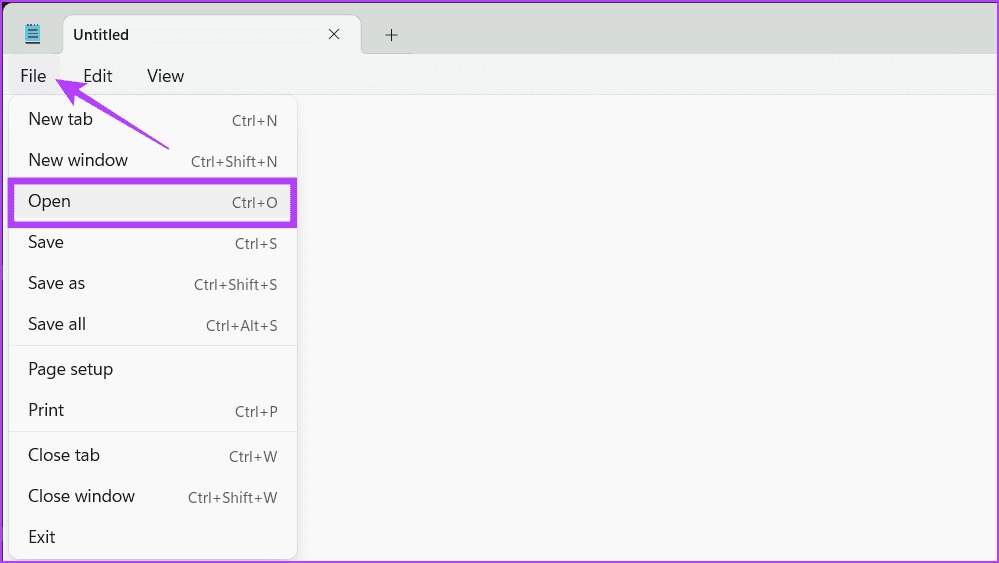
Step 3: Paste the following in the address bar.
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc
Note: Switch the file type to All files instead of .txt, the default file type.

Step 4: Select the hosts file and click Open.
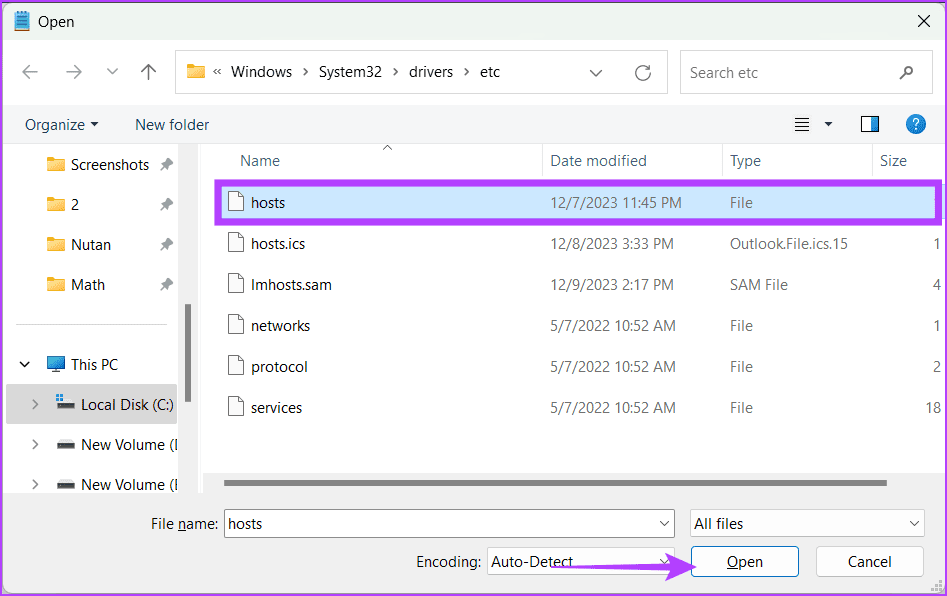
Step 5: Now, you can edit the host file. Once edited, click File and choose Save.
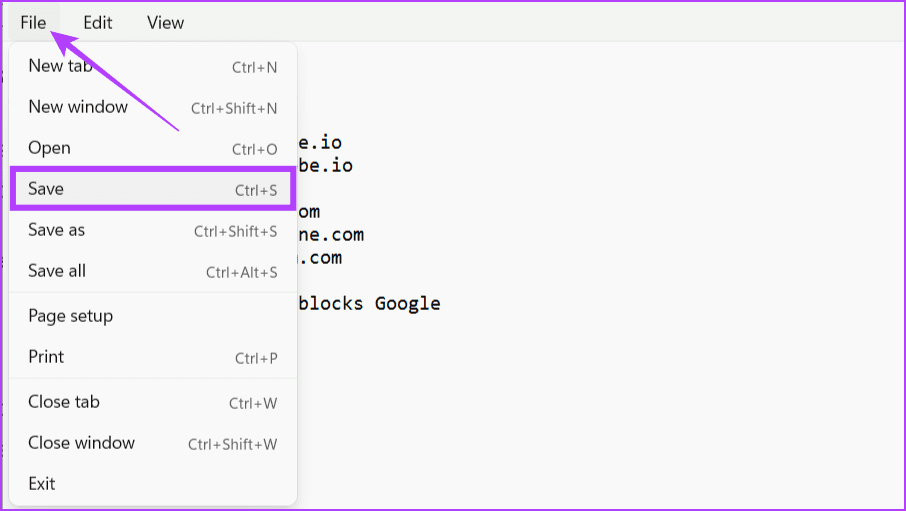
Also Read: How to fix Notepad not opening
Use of the Windows Hosts File
The Windows Hosts file is like a traffic cop for your computer’s internet connections. It has some useful jobs:
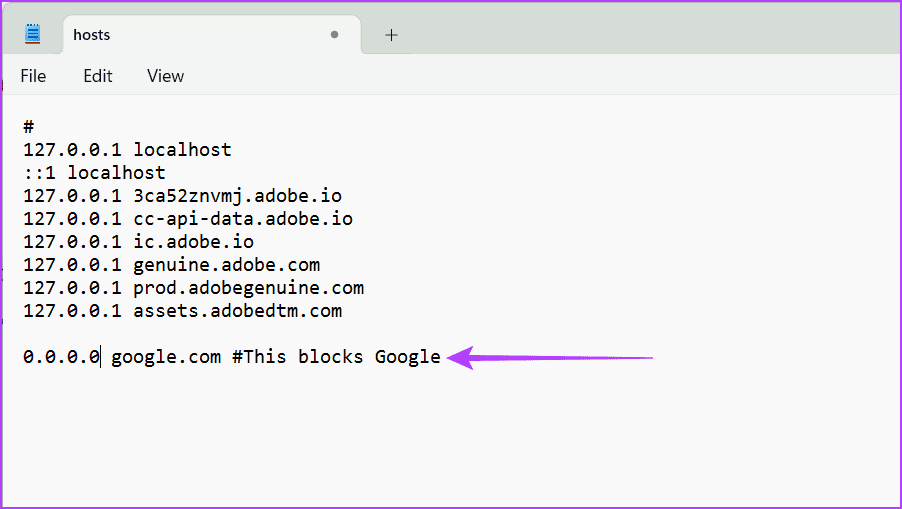
1. Blocking Websites
You can prevent access to unsolicited content and dangerous or distracting websites using the hosts file on your device. To accomplish this, add the below-mentioned file to your hosts file.
0.0.0.0 domainname.com
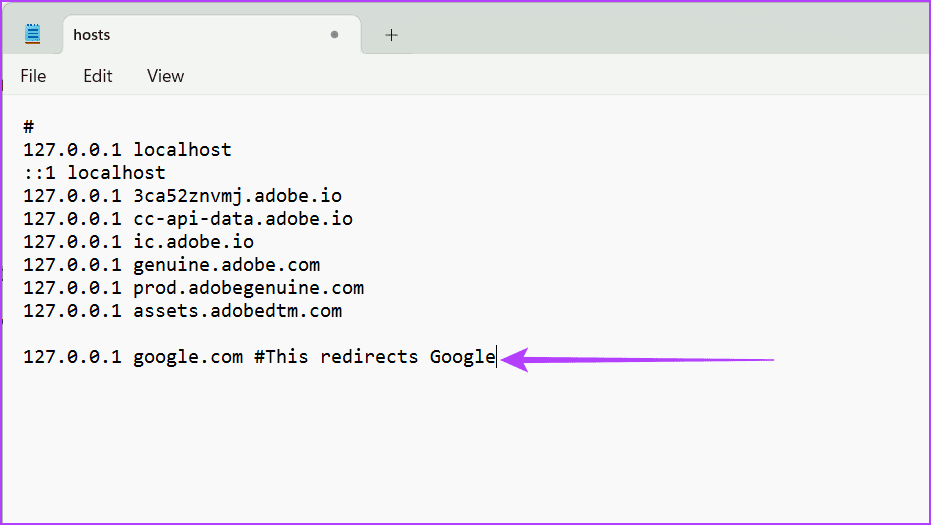
2. Redirecting Websites
Redirecting requests to a different IP address is another functionality the hosts file provides. This can be highly useful when creating a local testing environment or redirecting traffic away from malicious sites. To do so, add the following to your file:
127.0.0.1 domainname.com
3. Guarding Against Spam and Malware
Your system’s defenses can be strengthened by routinely updating the hosts file with the most recent listings of dangerous domains. You can manually block the suspicious and dangerous domains or reroute them to IP addresses that do not exist.
Modified Hosts File
If you followed the method mentioned above to locate and edit the hosts file on your Windows device but can still reach the sites you blocked or redirected using it, it could be due to DNS over HTTPS (DoH) being enabled in your browser.
DoH encrypts your DNS queries for privacy, allowing the browser to directly contact a secure DNS server and bypass the hosts file entirely, making it ineffective in blocking those websites. The new versions of popular browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Edge come with DoH enabled by default. You must disable DoH in your browser settings to use the hosts file effectively.
Was this helpful?
Last updated on 19 December, 2023
The article above may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. The content remains unbiased and authentic and will never affect our editorial integrity.