The hosts file is essential to how computers connect to a network. It’s like a map that helps match website names to specific numbers on your computer. If you’ve recently edited the hosts file on your Windows and things aren’t working well, don’t worry. This article will show you easy ways to fix the hosts file not working on Windows.

Whether you’re trying to block access to certain websites, redirect traffic, or manage local domain resolutions, troubleshooting the hosts file can become essential. From permissions problems to syntax errors, identifying the root cause of a malfunctioning hosts file can be challenging. So, follow along to troubleshoot the issue.
1. Flush DNS Cache
The DNS cache stores information about previously visited websites, and if this data becomes outdated or corrupted, it can lead to conflicts with the hosts file entries. By flushing the DNS cache, you are clearing this stored information and forcing the system to re-query and update the DNS records.
Additionally, it also ensures that the operating system fetches the most up-to-date information from the hosts file, enabling it to accurately map hostnames to IP addresses as specified in the file. Here’s how to do it on your device:
Step 1: Press Windows + S on your keyboard and type Command Prompt. Click Run as administrator and press Yes when you see the prompt.
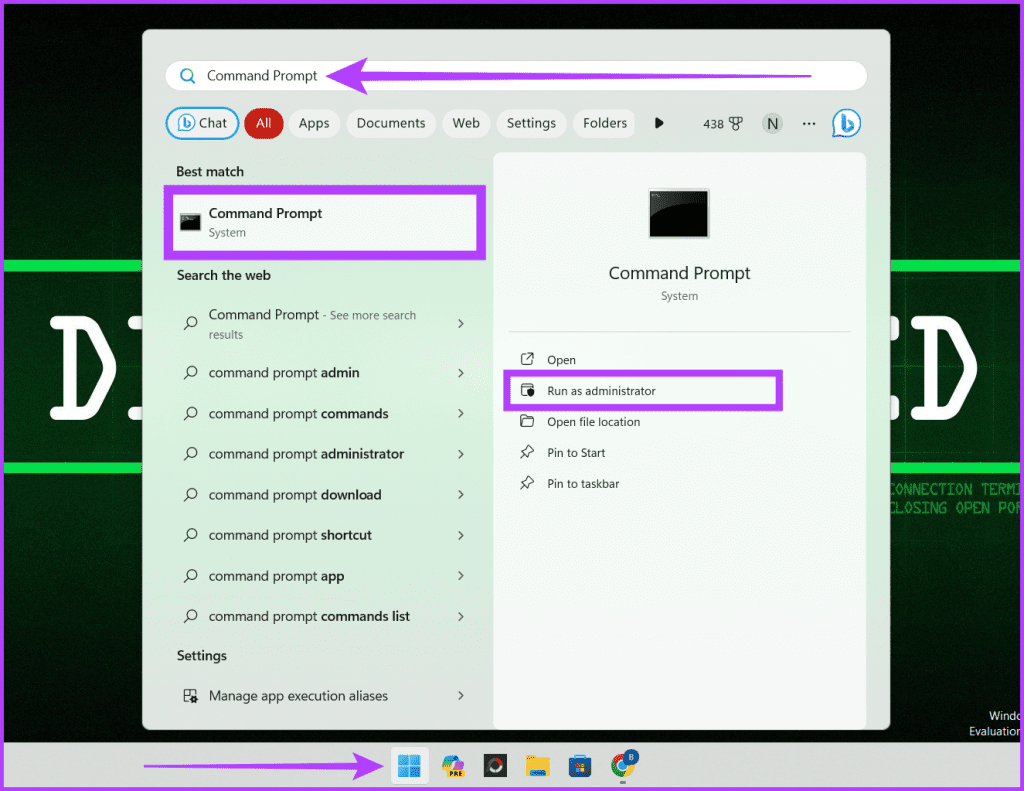
Step 2: Enter the below-mentioned command in your Command Prompt window and hit Enter.
ipconfig /flushdns

Now, you can see a confirmation message that says, “You’ve successfully flushed the DNS”. Once you see it, restart your device to apply the changes and check if the problem is fixed.
2. Reset NetBIOS Cache
If you’re having trouble with the hosts file not working right, resetting the NetBIOS cache can help. The NetBIOS cache is like a storage place for names and their matching IP addresses. If this storage gets messed up, it can cause problems with finding addresses, which affects the hosts file.
Resetting the NetBIOS cache makes the system build it again, fixing the hosts file not working on Windows. This ensures the hosts file can correctly match names to IP addresses. Follow the steps below to reset the NetBIOS cache on your Windows device and fix Windows hosts file:
Step 1: Click the Windows icon and enter Command Prompt in the search box. Select Run as administrator and choose Yes when prompted.

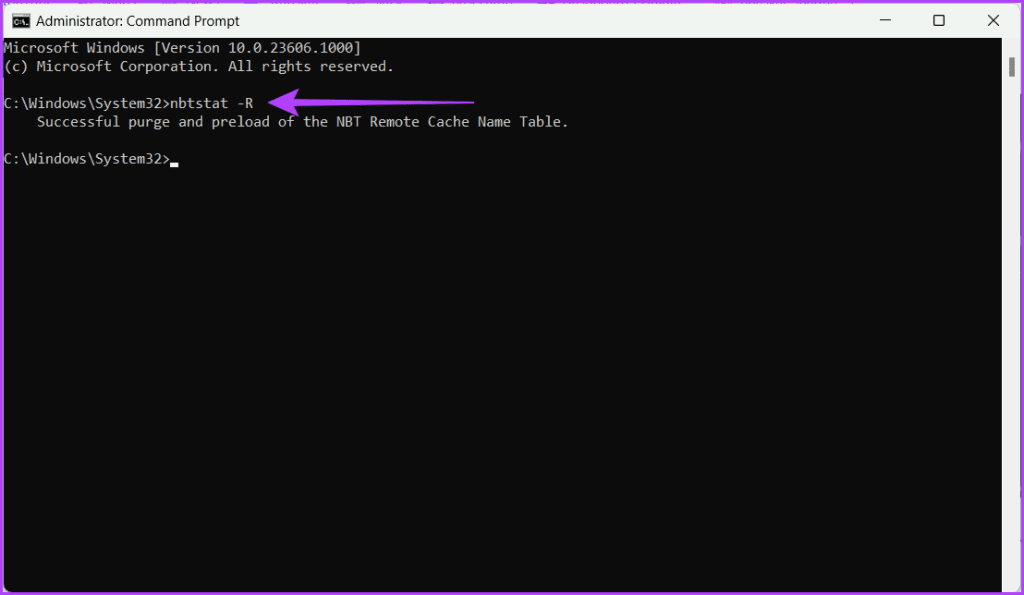
Step 2: Type the below mentioned in the CMD window and hit Enter.
nbtstat -R
3. Disable DNS Over HTTPS (DoH)
DoH protocol encrypts DNS queries, potentially bypassing local DNS configurations, such as those specified in the hosts file. This encryption can interfere with the system’s ability to resolve domain names according to the entries in the hosts file.
By disabling DoH, users can ensure that DNS queries adhere to the hosts file settings, allowing for accurate and customized domain name resolution. Here’s how you can do so on the Chrome browser:
Note: The steps are the same for other web browsers like Firefox.
Step 1: Launch the Chrome browser. Click the three-dot icon and choose Settings.

Step 2: Navigate to Privacy and security from the left and choose Security on the right.
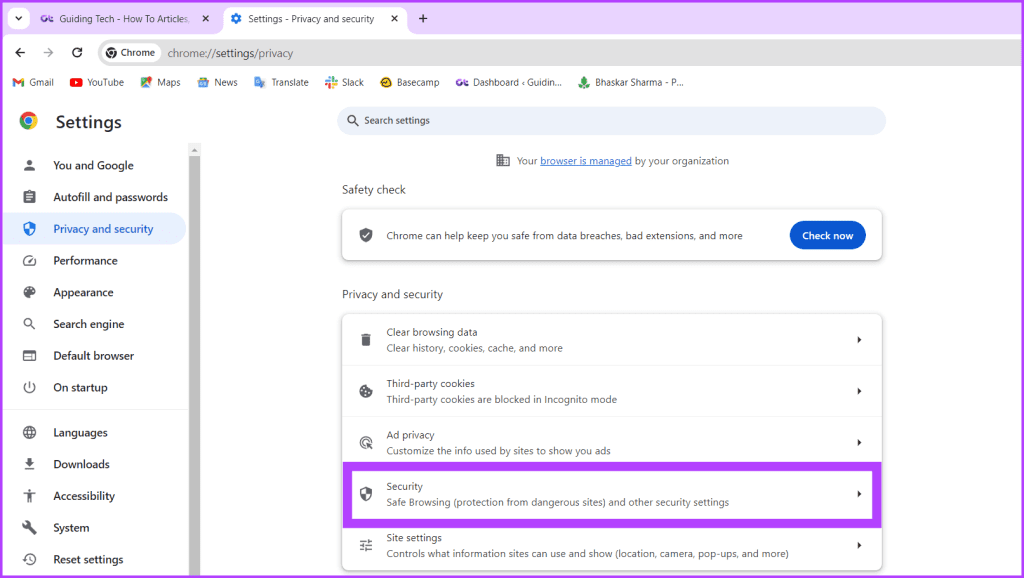
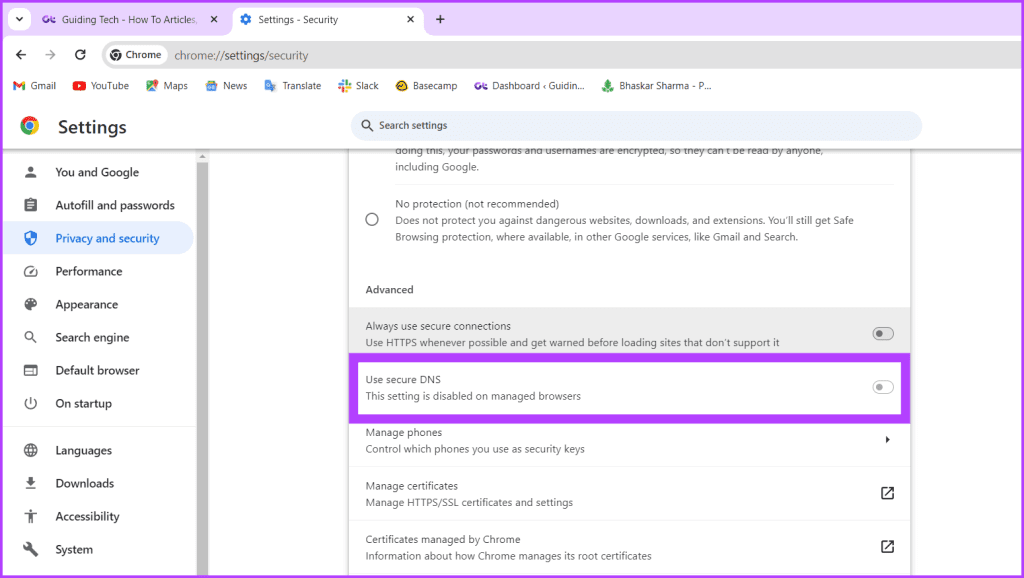
Step 3: Scroll down and toggle off Use secure DNS.
4. Check the Encoding Format of the Hosts File
Checking the encoding format of the hosts file is a crucial troubleshooting step when encountering issues in recovering host files. If the hosts file is not encoded correctly in ANSI or UTF-8 format, it can lead to errors, rendering the hosts file ineffective. To check the encoding format, follow the steps outlined below:
Note: UTF-8 is the recommended encoding, supporting a broader range of characters.
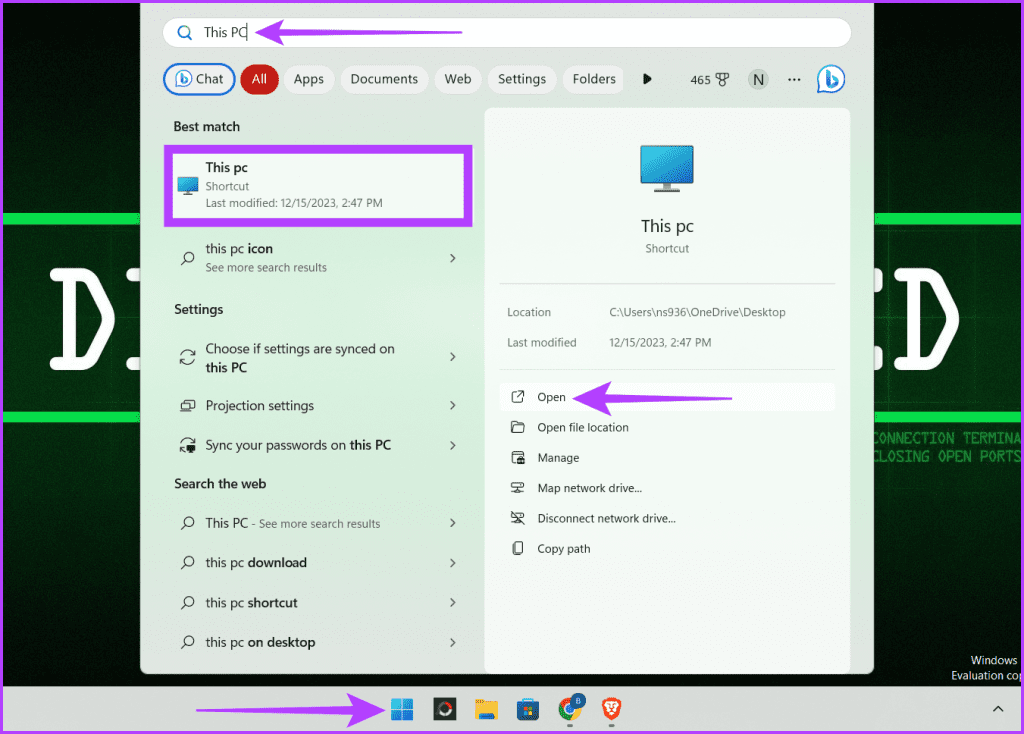
Step 1: Press the Windows + S key on your keyboard. Enter This PC in the search box and click Open.
Step 2: Paste the below-mentioned in the address bar and hit Enter:
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc

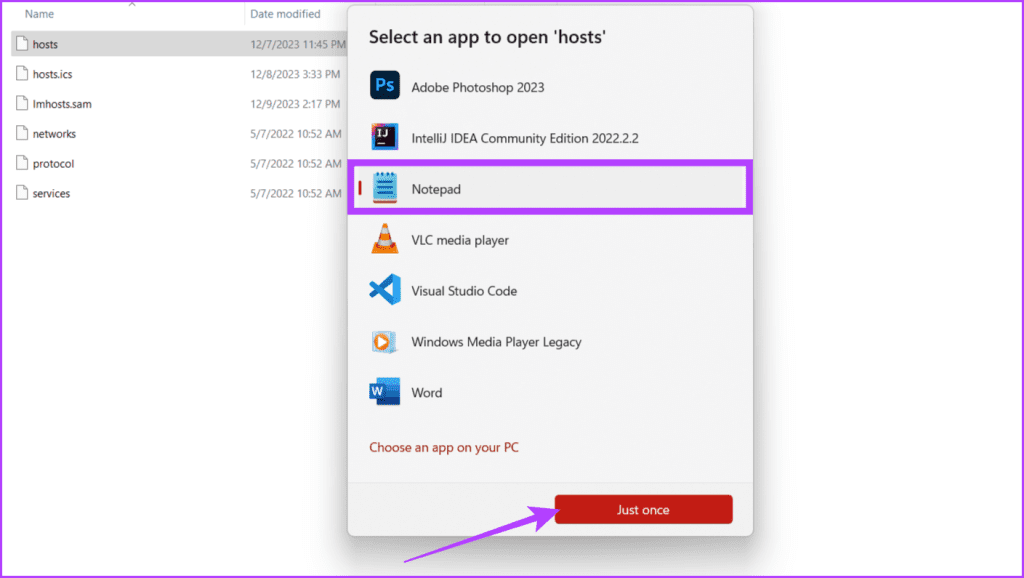
Step 3: Locate the hosts file. Right-click on it and select Open with.

Step 4: Select Notepad from the pop-up and click Just once.
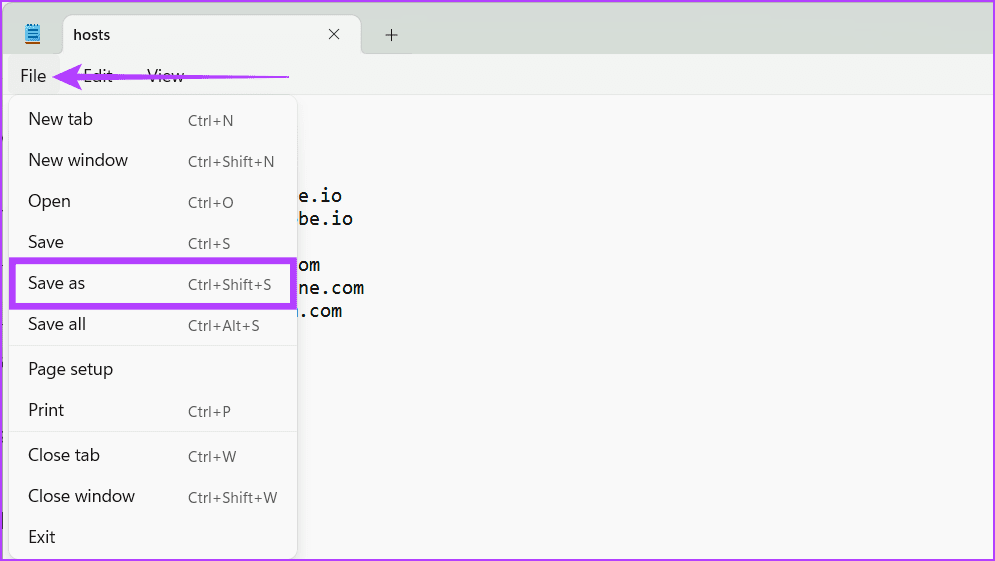
Step 5: Now, click File and select Save As.
Tip: You can also press Ctrl + Shift + S.
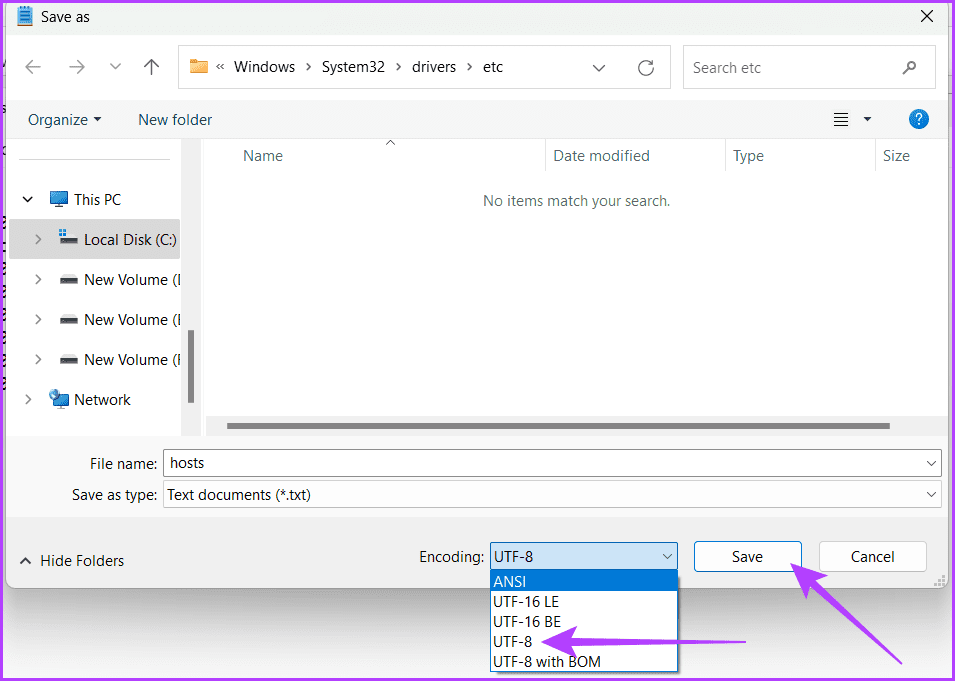
Step 6: Ensure the Encoding is UTF-8 or ANSI and hit Save.
5. Check for Permission Issues
It’s good to check permission-related issues if the hosts file on your device is not functioning as anticipated. The hosts file relies on having both the Read and Read & Execute permissions to operate optimally. Let’s delve into the simple steps to check the permission for the hosts file:
Step 1: Click the Windows icon. Search for This PC and click Open.

Step 2: Paste the below mentioned in the address bar and press the Enter key.
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc

Step 3: Right-click on the hosts file and select Properties.

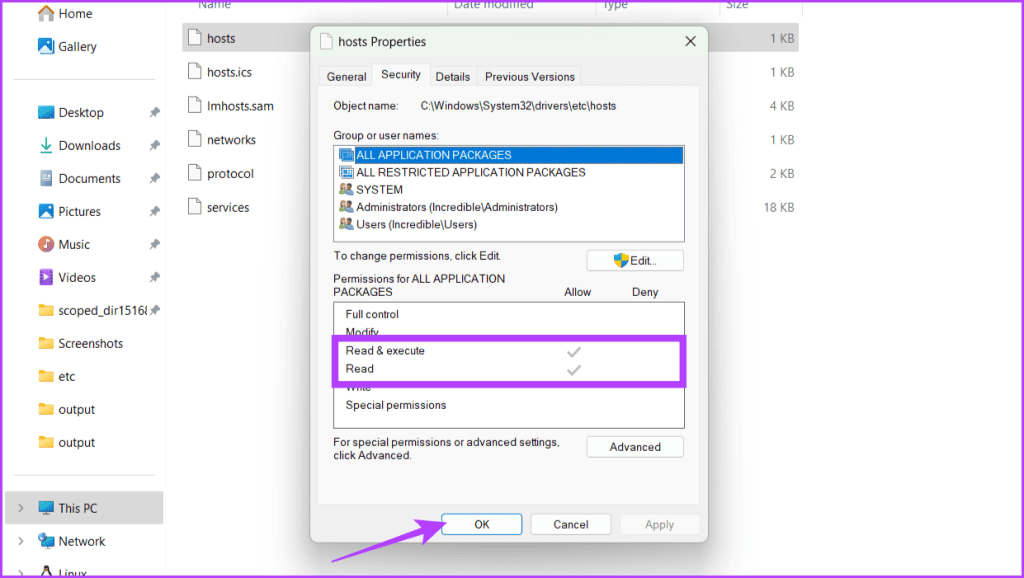
Step 4: Head to the Security tab and ensure that both Read & execute and Read are checked. Now click OK.
6. Reset the Hosts File
The hosts file is responsible for mapping hostnames to IP addresses, and if corrupted or misconfigured over time, it can lead to connectivity problems. One viable solution when encountering issues with its functionality is to reset the hosts file. Here’s how you can do so:
Step 1: Press the Windows key on your keyboard. In the search box, type This PC and click Open.

Step 2: To find hosts file, enter the below-mentioned location in the address bar and press Enter.
C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc

Step 3: Right-click on the hosts file and select the Delete icon.
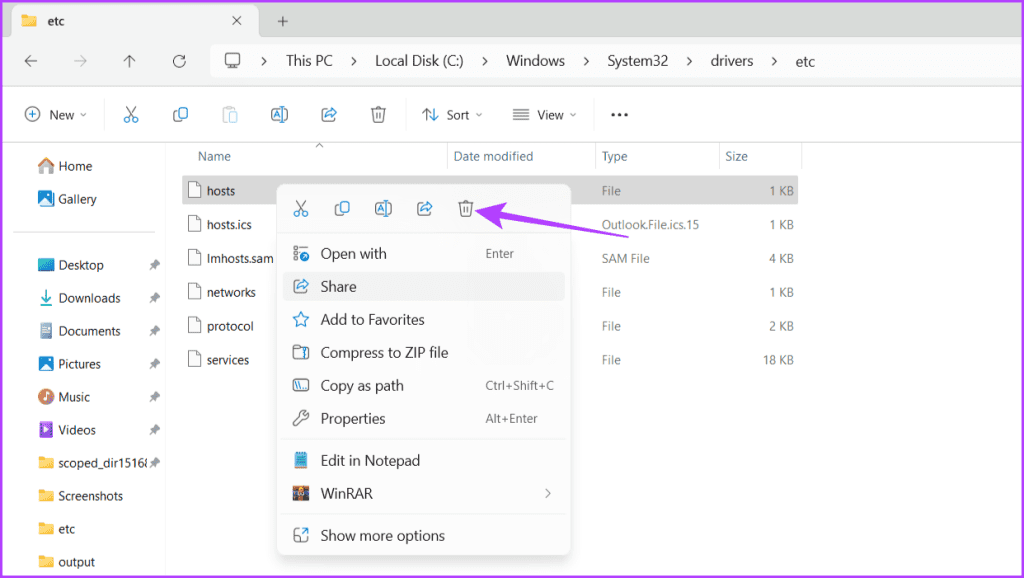
Step 4: Click Continue on the pop-up and select Yes in the prompt.
Step 5: Now, head to a new folder. Right-click in the empty area, select New, and choose Text Document.
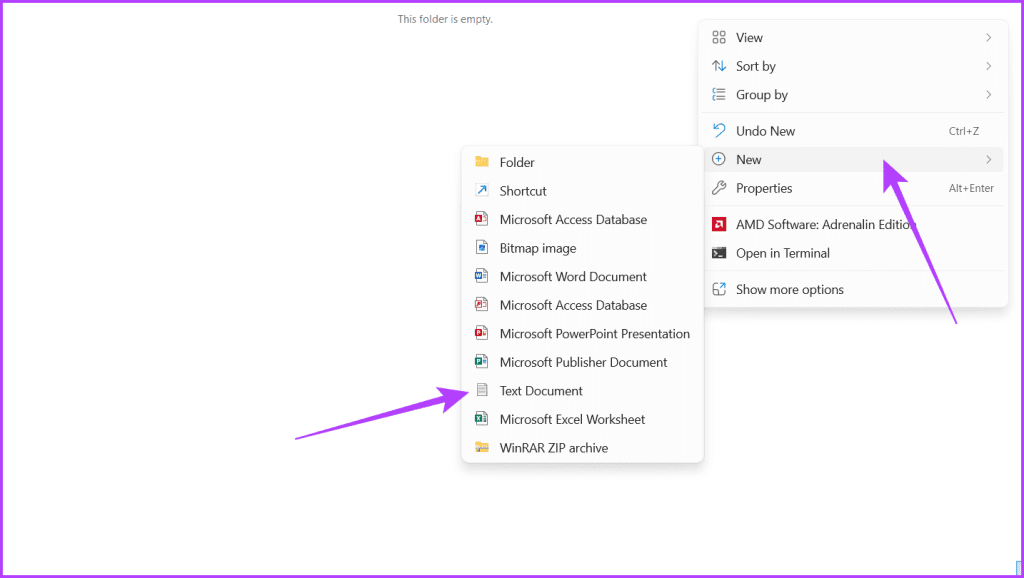
Step 6: Open the file and paste the below information into it.
# 127.0.0.1 localhost ::1 localhost 127.0.0.1 3ca52znvmj.adobe.io 127.0.0.1 cc-api-data.adobe.io 127.0.0.1 ic.adobe.io 127.0.0.1 genuine.adobe.com 127.0.0.1 prod.adobegenuine.com 127.0.0.1 assets.adobedtm.com
Step 7: Click File and select Save As.

Step 8: Rename the file to hosts. Ensure that the Encoding is UTF-8, and click Save.

Step 9: Now, copy the hosts file and paste it in the etc folder.
Grant the required permissions and restart your device. This should fix your Windows hosts file. If it’s still not working, follow along with the next method.
7. Disable the Proxy
Disabling the proxy lets the system use the hosts file directly. This means it can find website addresses based on the information in the hosts file. This is useful when you want exact control over how domain names are resolved. It ensures that the information in the hosts file is used first so the system can find addresses more reliably and accurately. Here’s how you can do so:
Step 1: Press the Windows key + I and open the Settings app.
Step 2: Head to Network & Internet and select Proxy.
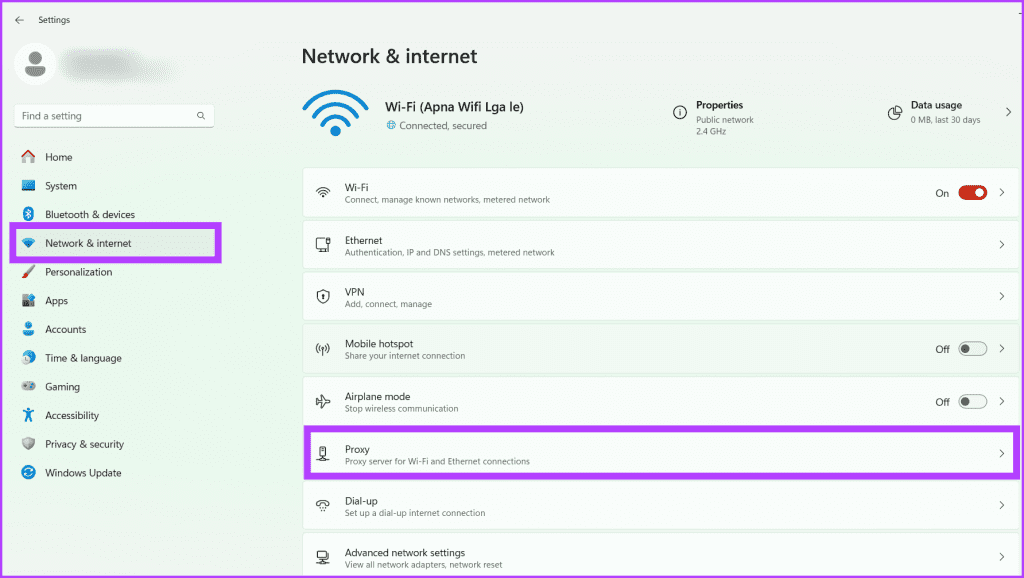
Step 3: Under Automatic proxy setup, turn off the toggle for Automatically detect settings.

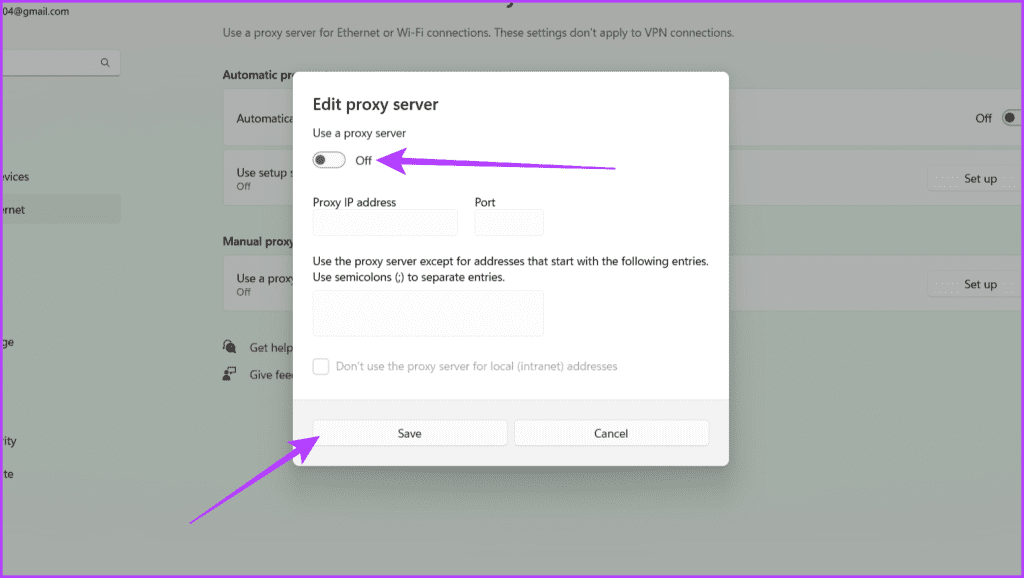
Step 4: Click Edit next to ‘Use a proxy server’ under Manual proxy setup.
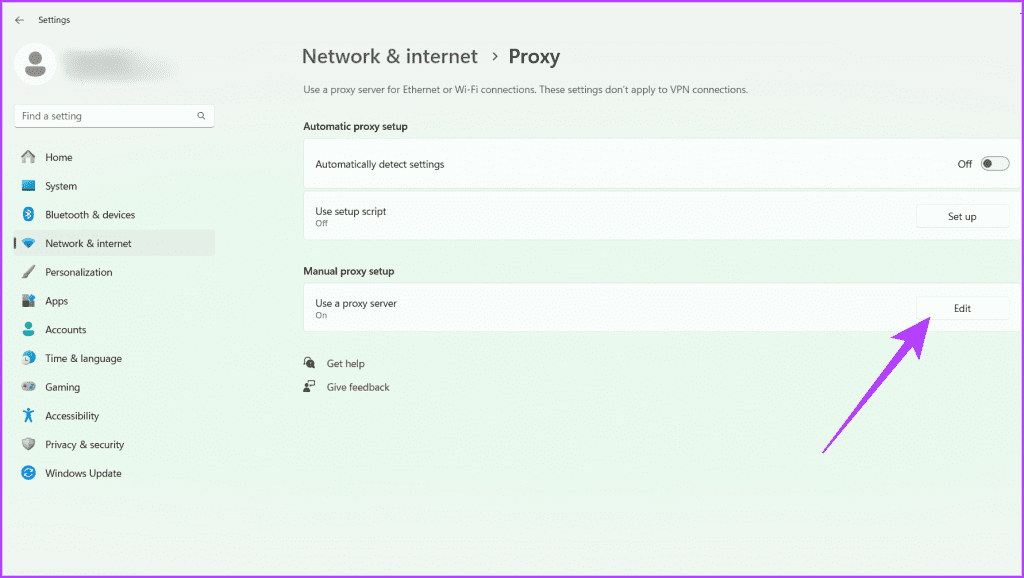
Step 5: Turn off the toggle for ‘Use a proxy server’ and click Save.
8. Flush Socket Pools in Chrome
Chrome, like many browsers, utilizes socket pools to optimize performance. These pools maintain open connections to frequently visited websites, enhancing speed and efficiency. However, cached information within these pools can sometimes conflict with recent updates to the hosts file, leading to inconsistencies.
Flushing the socket pools forces Chrome to discard any cached connection data and initiate fresh website connections. This process ensures that Chrome adheres to the updated hosts file entries, resolving discrepancies. Here’s how you can do so:
Step 1: Launch the Chrome browser.
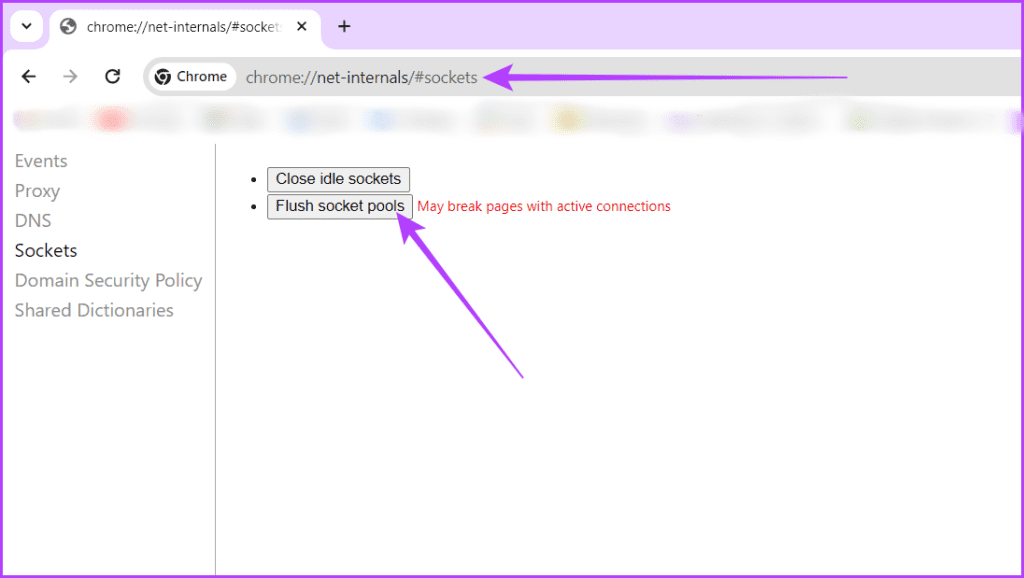
Step 2: Head to the hosts file location by typing the below text in your Chrome address bar and hit Enter.
chrome://net-internals/#sockets
Step 3: Click the Flush socket pools button.
Step 4: Now, restart your Chrome browser for the changes to take effect.
Also Read: How to fix Chrome not opening on Windows.
Hosts File Found
The hosts file not working on your Windows device can be frustrating. We hope the suggested solutions mentioned earlier have helped you fix the problem. Let us know which of the above fixes worked for you.
Was this helpful?
Last updated on 26 December, 2023
The article above may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. The content remains unbiased and authentic and will never affect our editorial integrity.