How to Use the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool
You can open the diagnostic tool from the search, Command Prompt, Control Panel, and Recovery.
Step 1: Press the Windows + R keys together to access the Run utility.
Step 2: When a Run dialog appears on your screen, type mdsched.exe and press Enter.
Step 3: You should see a Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool window pop up on your screen with two options:
- Restart now and check for problems (Recommended): Select this if you want to reboot your PC immediately to troubleshoot memory-related issues.
- Check for problems the next time I start my computer: Select this if you want to schedule the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool to run the next time your PC starts.

Step 4: Whichever option you choose, once your PC restarts, the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool will automatically start scanning your system for memory-related issues in Standard mode.

Step 5: If you want to change the scan options to Basic or Extended and change the number of scan passes, press the F1 key on your keyboard to access more options.

Note: You will have to press the Tab key on your keyboard to cycle through the different scan options, F10 to Apply the new changes, or Esc to go back and cancel the changes.
How to Check the Memory Diagnostic Results
After the scan completes, your PC will restart, and a pop-up notification showing the results should appear at the bottom-right corner of the desktop view. However, it’s a hit or miss and doesn’t give you a detailed look at the scan results. In such cases, check the Event Viewer.
Step 1: Press the Windows + S keys to launch Windows Search and type Event Viewer. Then, from the result that appears, click on Open.
Step 2: When an Event Viewer window opens, click on Windows Logs, followed by System. Then click on Find in the right-most pane.

Step 3: When a Find dialog appears on the screen, type MemoryDiagnostics-Results. Then click on Find Next. This will help you find the most recent Memory Diagnostic report.
Step 4: When you find the relevant report, click Cancel. You’ll see the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool scan result on your screen.
Step 5: Click on the Details tab to find more in-depth results for the scan.
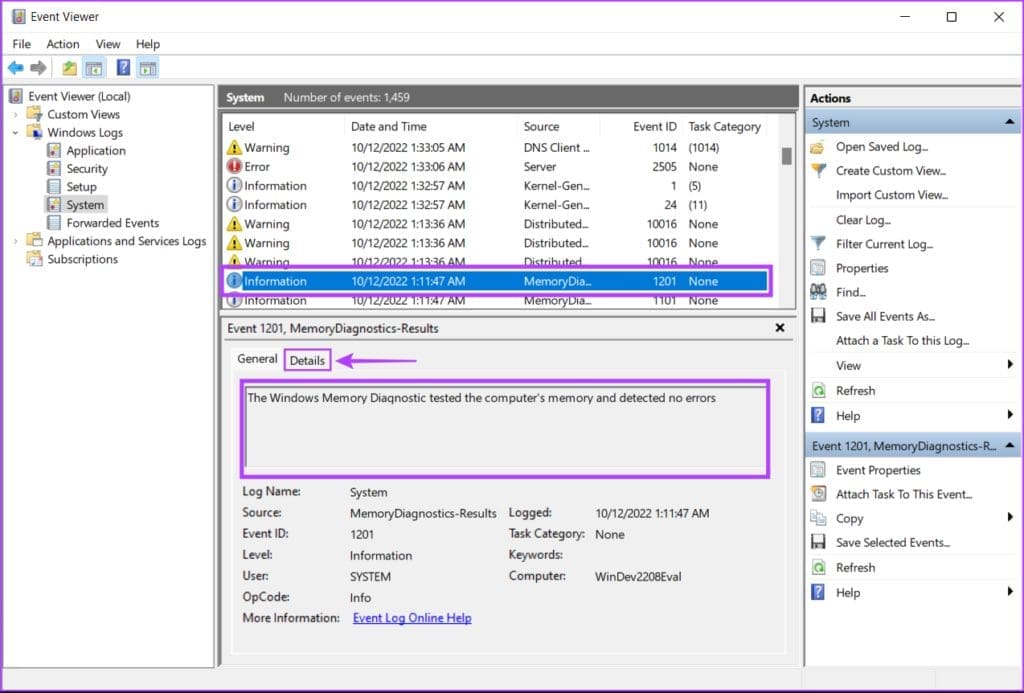
If the memory installed on your system has no issues, you will get a message saying, “The Windows Memory Diagnostic tested the computer’s memory and detected no errors.” But if errors are detected, you’ll find details about the problem with the RAM installed on your system.
You may clean and reseat the RAM sticks and rerun the Windows Memory Diagnostic scan to check if the problems are fixed. If that doesn’t help, it might be time to replace the RAM on your system.
To replace or upgrade the RAM on your PC, check our guide to find available RAM slots alongside the best ways to check the RAM size on Windows 11.
FAQs
How Do You Exit the Windows Memory Diagnostic?
To interrupt the ongoing memory diagnostics test, press F1 or Fn + F1. Then, press Esc to restart your computer and boot back into Windows.
How to Stop Memory Diagnostic From Running on Every Restart?
If your PC is stuck in the memory test loop, you can prevent future memory diagnostic tests by opening the Task Scheduler and deleting the Memory Diagnostics task.
Was this helpful?
Last updated on 20 April, 2024
1 Comment
Leave a Reply
The article above may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. The content remains unbiased and authentic and will never affect our editorial integrity.









Thanks that was helpfull!