Fix 1: Disable Fast Startup
Fast Startup is a useful feature that puts your computer into a hibernation state rather than a full shutdown. This allows your computer to boot up quickly the next time you turn it on. However, it can sometimes prevent Windows from shutting down completely, causing problems.
You can try disabling Fast Startup temporarily to see if that fixes the issue.
Step 1: Press the Windows key + R to open the Run dialog. Type control in the box and press Enter.
Step 2: Use the drop-down menu in the top right corner to change the view type to Large icons. Then, select Power Options.

Step 3: Click the Choose what the power buttons do option in the left sidebar.

Step 4: Click on Change settings that are currently unavailable.

Step 5: Uncheck the box that reads Turn on fast startup (recommended), and click the Save changes button at the bottom.

Restart your PC after this, and then try shutting it down.
Fix 2: Configure Power Management Settings for USB Devices
Another reason why your Windows laptop or PC may not be shutting down fully is due to the connected USB devices. To avoid this, you need to change the power management settings for all of your USB devices. Here are the steps for the same.
Step 1: Right-click on the Start icon and select Device Manager from the list.
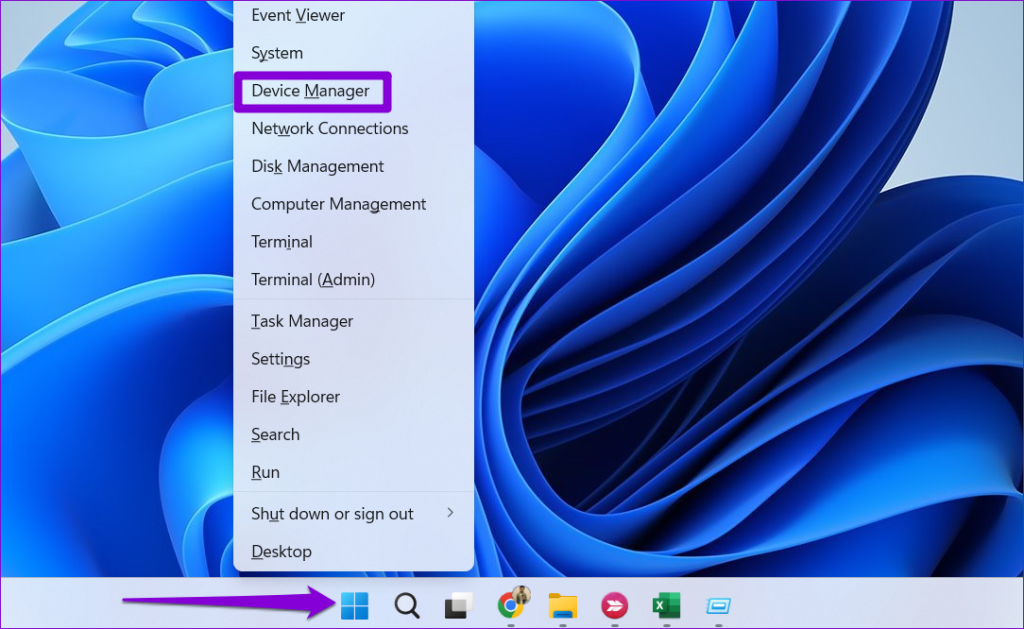
Step 2: Expand Universal Serial Bus controllers. Right-click on the first entry and select Properties.
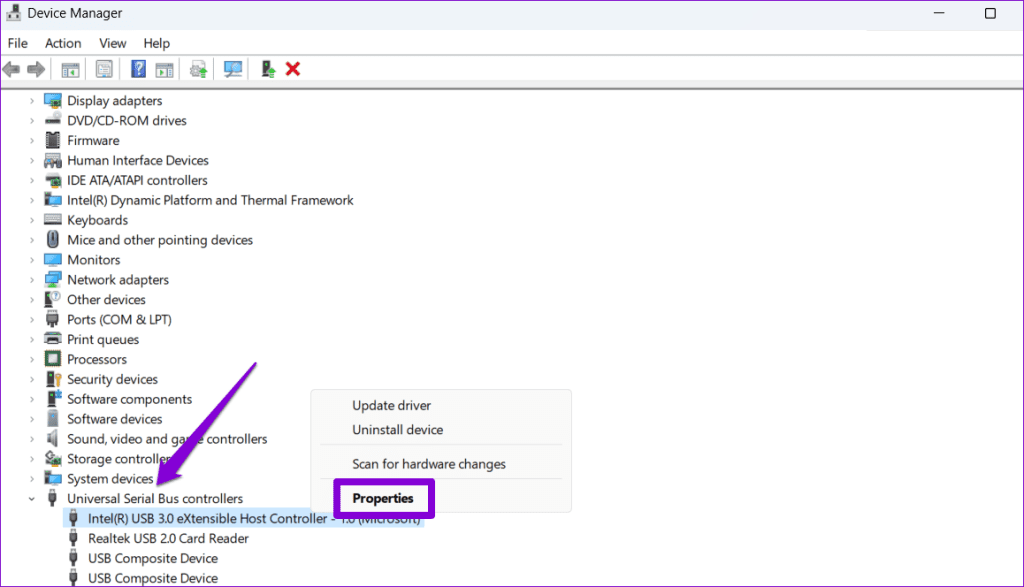
Step 3: Switch to the Power Management tab and untick the checkbox that reads Allow the computer to turn off this device to save power. Then, click OK.
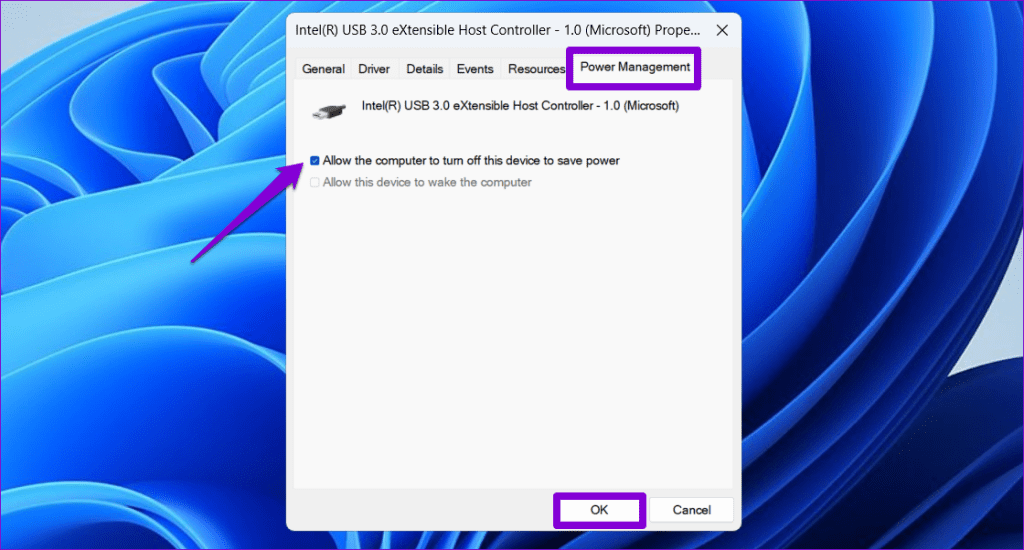
Repeat these steps for all of your USB devices. Following that, your Windows PC or laptop should not stay on after a shutdown.
Fix 3: Reinstall Graphics Drivers
Outdated or corrupted graphics drivers can also cause your Windows PC to stay on after a shutdown. If that’s the case, uninstalling the graphics driver and reinstalling it should restore normalcy.
Step 1: Right-click on the Start icon and select Device Manager from the list.
Step 2: Expand Display adapters, right-click on your graphics driver, and select Uninstall device.

Note: If there is an exclamation point next to any entries in Device Manager, it means that those drivers are not working properly. In that case, you will need to update those drivers as well.
Restart your PC after removing the graphics driver. Windows will automatically reinstall the missing driver during startup.
Fix 4: Update BIOS/UEFI
If nothing works, you should download the most recent BIOS or UEFI version for your device and copy it to a USB flash drive. Since the steps for updating BIOS can differ depending on your PC’s make and model, it is best to refer to your computer manufacturer’s support page for detailed instructions.
Was this helpful?
Last updated on 25 July, 2024
1 Comment
Leave a Reply
The article above may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. The content remains unbiased and authentic and will never affect our editorial integrity.







Thanks to you..my problem is solved..