On Windows 11 computers, you may use the RAID 1 data storage technology to create similar copies of data on multiple hard drives, also known as mirroring. This tech has become a favorite for businesses and individuals as it offers increased data availability, and you are guaranteed a safe backup even if there is a crash on your computer.

While this tech is very useful, it is pretty simple to use, and even for the less tech-savvy individuals, with just a few clicks, they should be well on their way. We show you how to setup RAID 1 on Windows 11 in this guide, as well as all you may need before starting the process.
Hardware Requirements for a RAID Set Up
Before you go into creating RAID 1 setup on Windows 11, take note of the following requirements:
- You should have a minimum of two drives.
- All drives involved needs to have the same file type – NTFS works great.
- There must be a RAID controller; on Windows 11, you may use the built-in Storage Spaces feature as a software alternative.
- A motherboard that is compatible with RAID. This may be a problem for older motherboards.
1. Configure RAID 1 on Windows 11 via the Settings App
The Settings app is a central location that allows you to configure multiple options on the operating system. From appearance and behavior personalization to managing privacy and security, there is so much the app can accomplish. You may also use it to configure RAID options and create RAID 1, as shown below.
Step 1: Press Windows + I keyboard shortcut on your keyboard to open the Settings app.
Step 2: Click the Storage option on the right pane.

Step 3: Scroll down the right pane and click ‘Advanced Storage Settings.’

Step 4: Click Storage Spaces on the right pane.
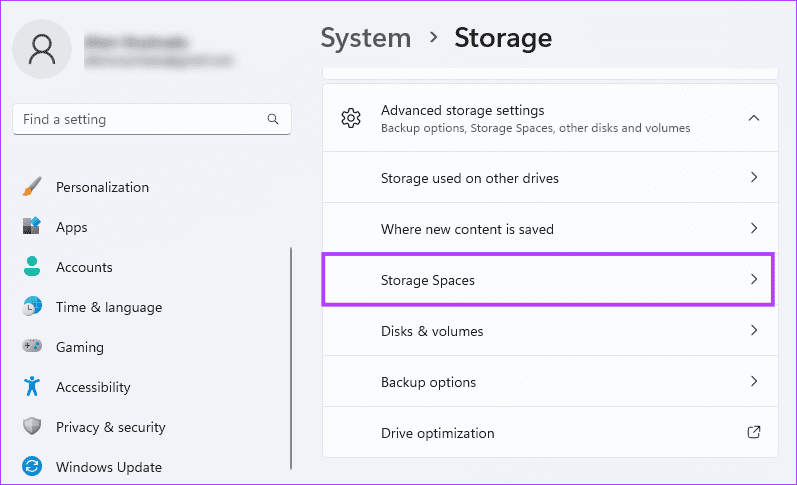
Step 5: Click the Add button to begin the creation of a RAID storage.
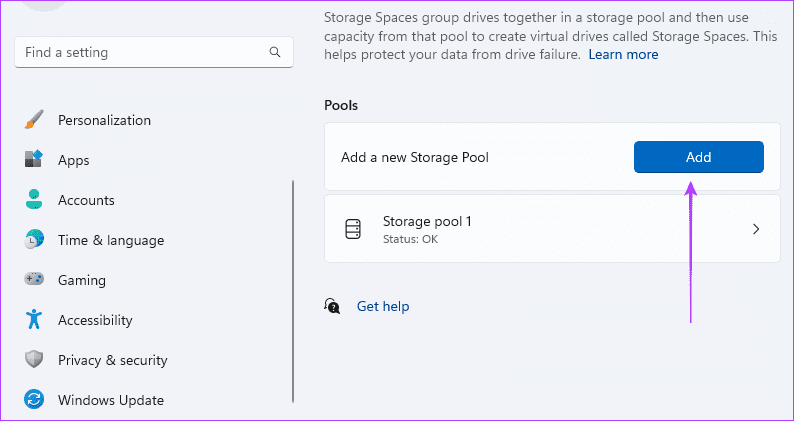
Step 6: Fill in the Name field, select the disk from which you want to create RAID 1, then click the Create button.

Step 7: Here, you fill in details for the Space the pool in the previous window will belong. Enter a value for Name, pick the Size you desire, select ‘Two-way mirror’ for Resiliency, and click Create.

2. Set Up RAID 1 Using the Control Panel
Control Panel is a utility that gives users access to change and reconfigure certain options on the device. It comprises hardware and software configuration applets and may be used for managing specific drive functions, like creating RAIDS, as shown below.
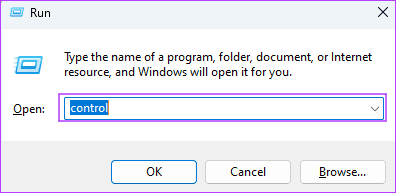
Step 1: Press Windows + R keyboard shortcut to open the Run dialog, type control and hit Enter.
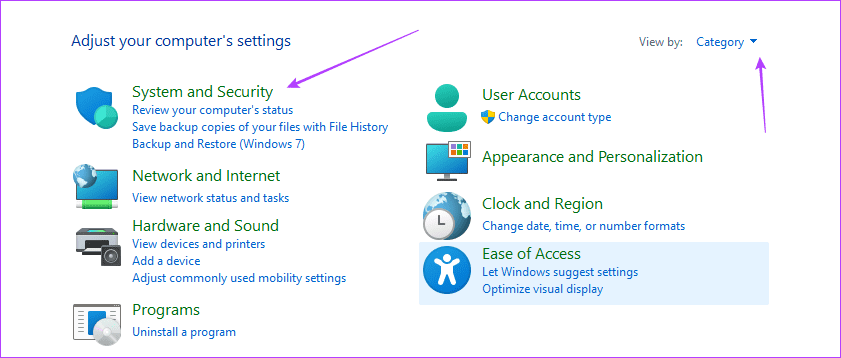
Step 2: Make sure the View by option is set to Category in the top-right corner and click ‘System and Security.’
Step 4: Click Storage Spaces.

Step 5: Click ‘Create a new pool and storage space.’

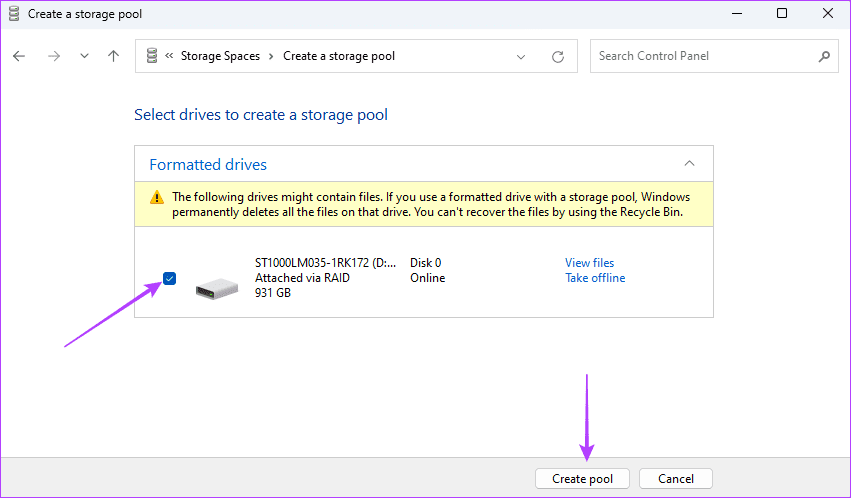
Step 6: Select your drive and click Create Pool.
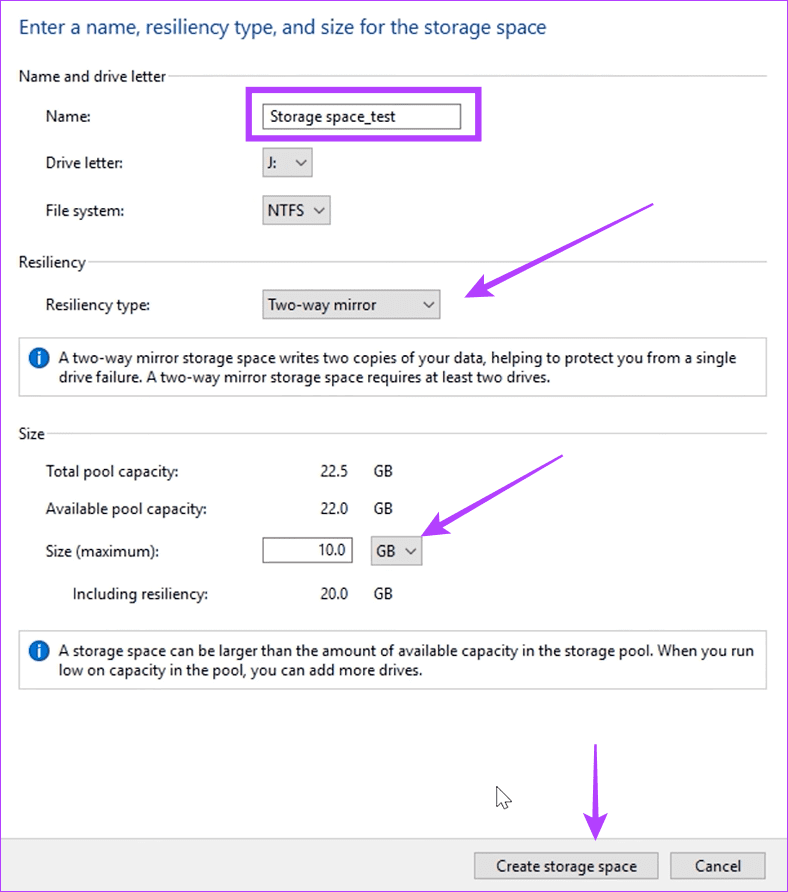
Step 7: Name the Storage Space, use the drop-down next to Resiliency type to choose Two-way mirror, select an appropriate size, then click ‘Create storage space.’
3. Configure RAID 1 From the Disk Management Settings
On Windows 11, you may use the Disk Management utility to manage hard drives and disks. The tool lets you create, resize, delete, format, and manage the drives on your computer. You may also employ this tool to create RAID 1 on Windows 11.
Step 1: Right-click the Start menu on your Taskbar, then select Disk Management.
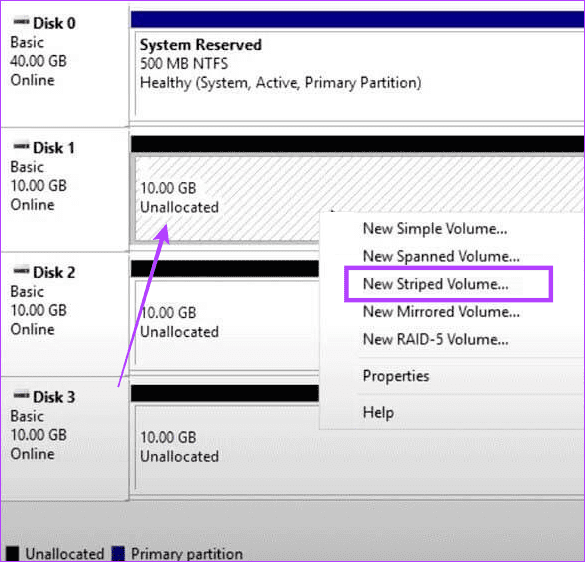
Step 2: Right-click on the Drive for your RAID, and select ‘New Striped Volume’.
Step 3: Click Next.
Step 4: Select the disk to RAID, click add, then click Next.
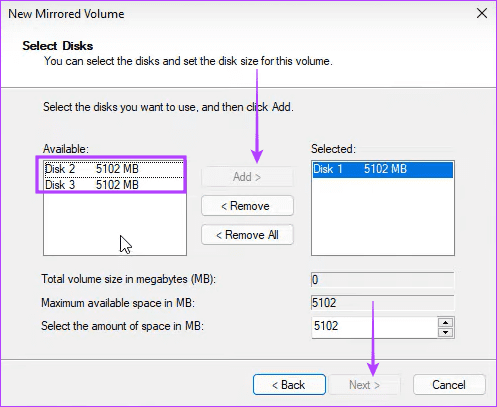
Step 5: Select NTFS and click Next.
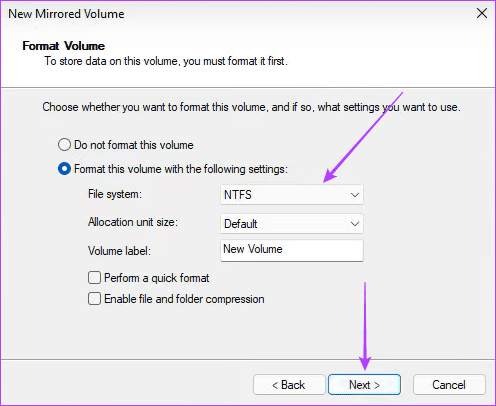
Step 6: Click Finish and confirm your choice.
4. Set Up RAID 1 via the Command Prompt
The Command Prompt is a text-based interface allowing users to interact with the Windows operating system. It is a powerful tool that may be employed for system configuration, file management, troubleshooting, or even disk management. As shown below, you may use it to create a RAID 1 drive.
Step 1: Press Windows + R keyboard shortcut to open the Run dialog.
Step 2: Type cmd and hit Control + Shift + Enter keyboard shortcut to open the Command Prompt with admin privileges.

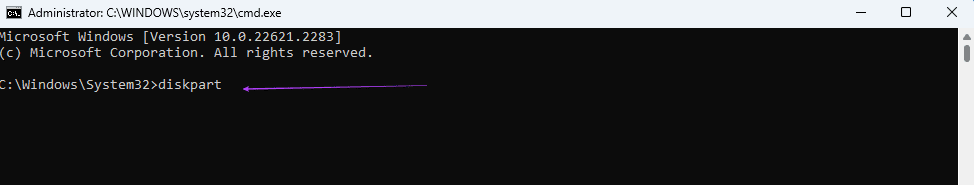
Step 3: Type the below command and hit Enter to access drive and disk management:
diskpart
Step 4: Type the below command to see all available drives:
listdisk

Step 5: Type the command below, replacing N with a disk number for the RAID:
Select disk N
Step 6: Type the command below to convert the selected drive to a dynamic one:
convert dynamic
Step 7: Repeat steps 5 and 6 for other drives you need to be part of the RAID process.
Step 8: Enter the command below to create your RAID volume:
Create Volume RAID Disk 1, 2, 3

Step 8: Select the newly created RAID using the script below:
select volume 2
Step 9: Change the format and assign it a drive letter by running the two scripts below one after the other:
Format FS=NTFS Label=NewVolume
Assign Letter=E

Using the New Virtual Disk
The solutions above will help you configure RAID 1 on Windows 11. So now, you should be able to use your newly created virtual drive if you run into disk drive failure. Other RAID types exist, like RAID 2, 3, 4, or 5. The main difference is in the level of data redundancy and number of drives required. RAID 1 offers a 100% data redundancy.
Was this helpful?
Last updated on 26 September, 2023
The article above may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. The content remains unbiased and authentic and will never affect our editorial integrity.