Windows File Explorer is an integral part of Windows. With this explorer, you can view all your files and folders, carry on simple operations like copy and paste, and check the file size, and file management. At times, you might not be able to utilize any of these features when the File Explorer is not responding on your Windows PC.

The issue mostly occurs due to a lack of available memory for File Explorer and all of its components. However, the problem may also arise due to a bug in your PC. In this article, we want to show you all the ways by which you can get rid of the issue and use File Explorer without any problems.
Also Read: 10 ways to fix File Explorer stuck at ‘Working on It’ error
1. Restart Windows Explorer
One of the first things that you can do is restart the Explorer. If it’s a simple issue of corrupted cache files, the odds are that it will solve your issue.
To restart File Explorer, bring up the Task Manager, and you will see Windows Explorer under Processes.
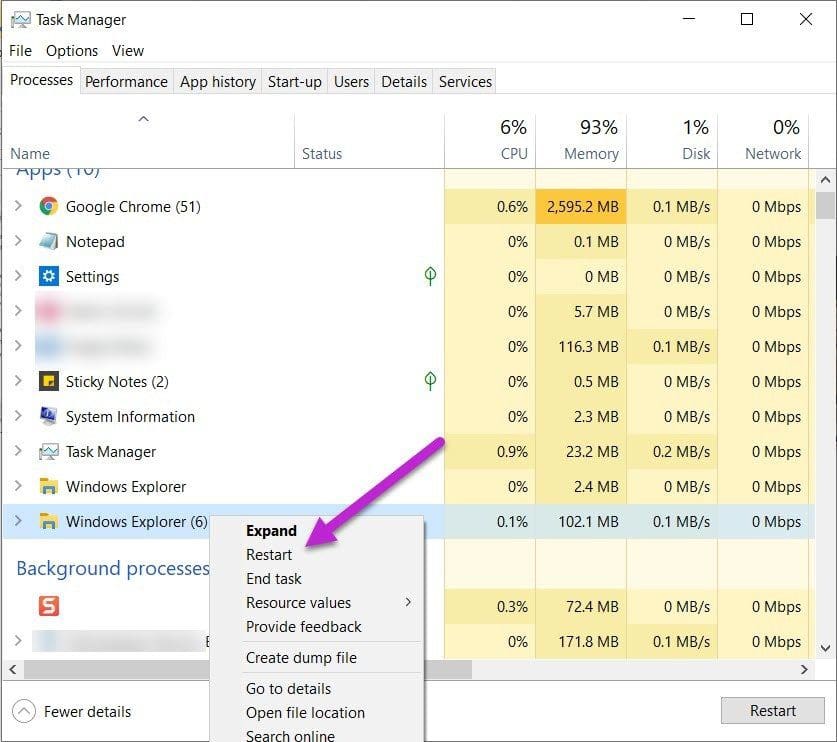
Right-click on it and select Restart from the menu.
2. Restart File Explorer Using CMD
Restarting File Explorer through Command Prompt (CMD) can sometimes be more effective than simply restarting it using Task Manager because it ensures a cleaner restart of the process. Here’s how you can do it.
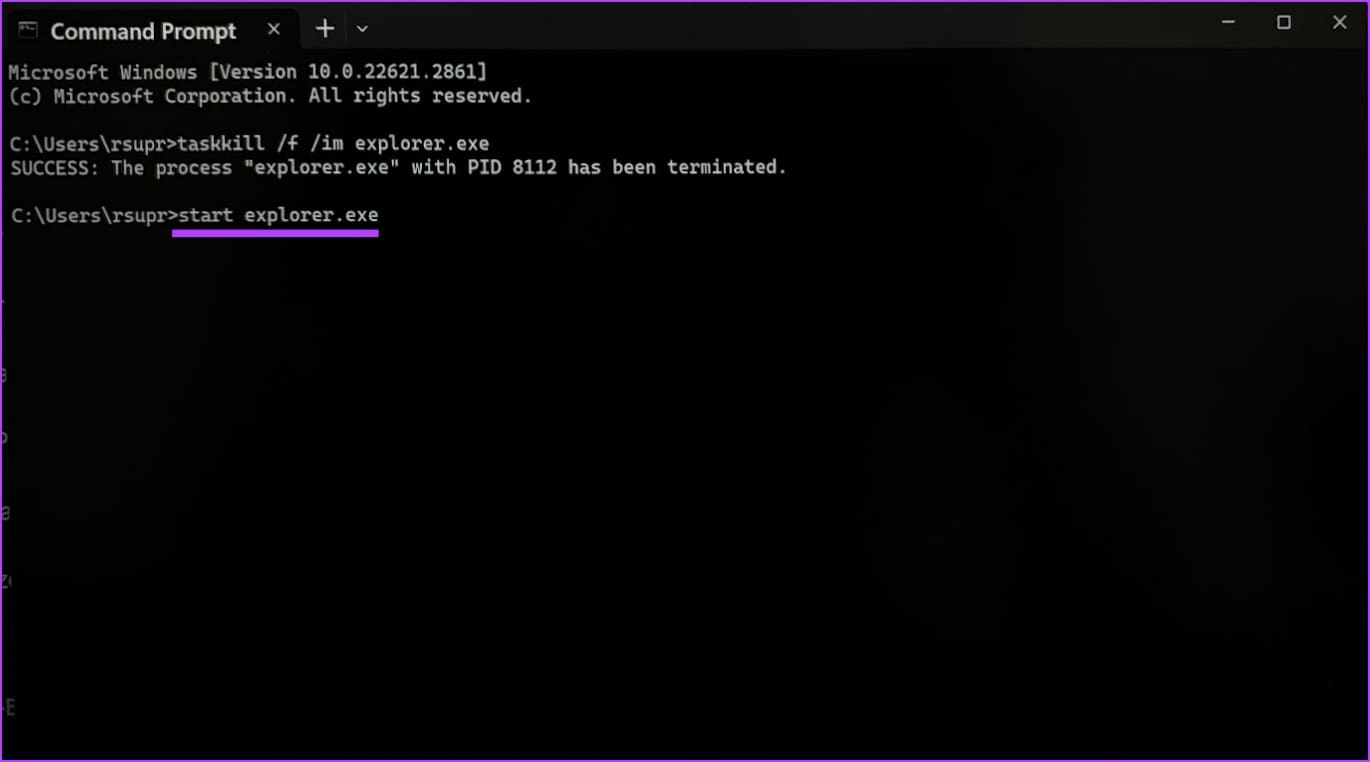
Step 1: Open Command Prompt from the start menu.
Step 2: Enter the following command :
taskkill /f /im explorer.exe
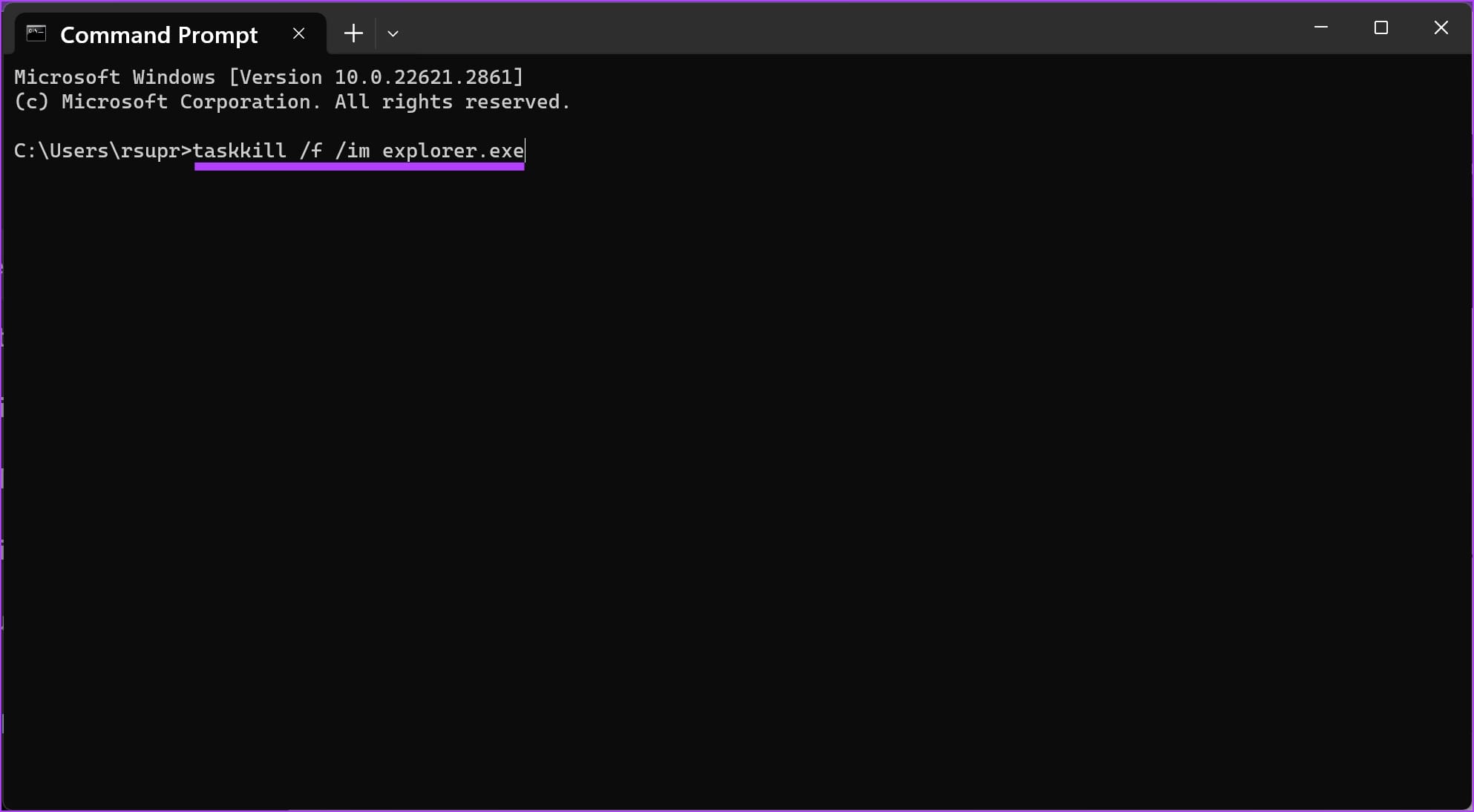
This will close the file explorer. Do not minimize or close the command prompt window.
Step 3: Enter the following command to restart the File Explorer.
start explorer.exe
3. Close Other Apps to Increase Available Memory
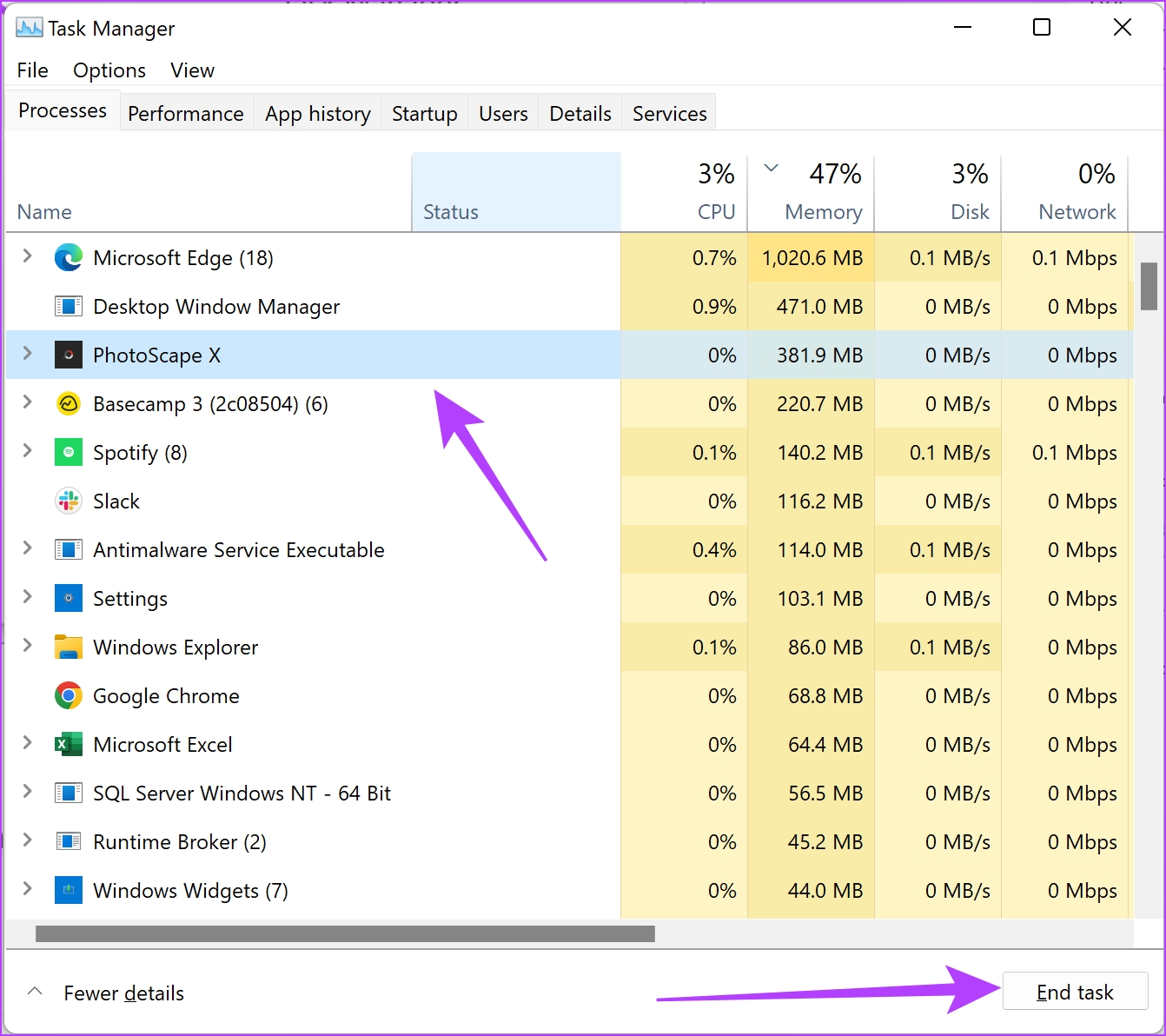
Make sure to close unwanted applications on your Windows PC to free up memory for File Explorer. For best results, you can open Task Manager, right-click on the app and select End Task. However, make sure you only close applications and windows that are open – and not any other background processes.
4. Check for Updates
Windows Updates are a necessary part of the system since they bring essential security updates. But if you have updates pending for a long time, you may see your system slowing down or acting weirdly. This is especially true if Windows is undertaking memory-intensive jobs.
Open the Settings app, and go to the Windows Update section. You will be able to check for updates and download if a new one is available.

These days, it’s quite easy to spot a pending update. If you see a small orange dot on your system’s taskbar, you know what to do.
Alternatively, you can search for ‘Check for updates’ on the Start menu to see pending updates.
5. Clear File Explorer History
Explorer’s search comes in handy at many times. It saves every detail such as the names of files you have searched, and paths you have searched, among others. These search files can accumulate in time and cause the Windows File Explorer to respond slowly. Luckily, clearing the history is as easy as 1-2-3.
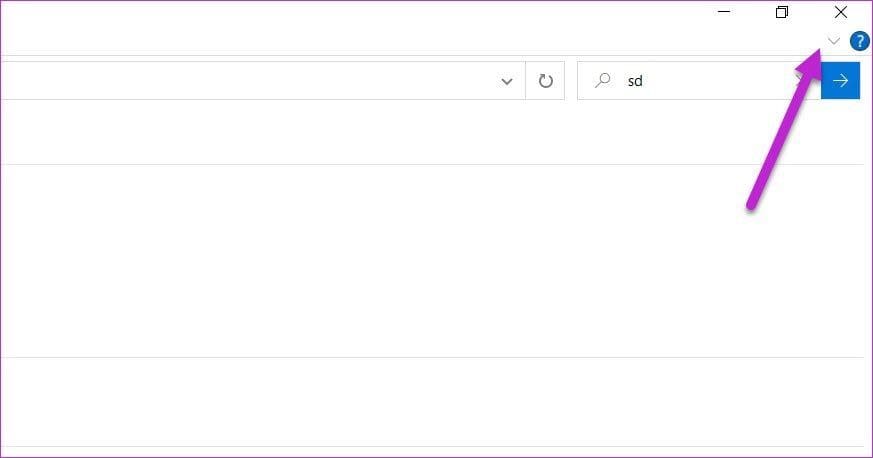
Step 1: To get started, search for anything in the search box of Explorer. When the search is complete, click on the little arrow icon as shown below to expand the ribbon.
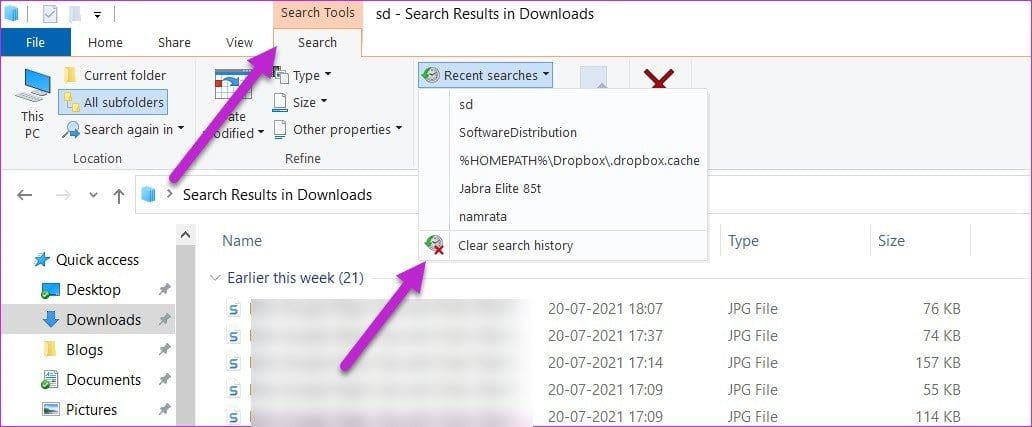
Step 2: Next, click on the Search tab, and select Recent Searches > Clear Search History.
Step 3: The above will work only when your system’s Explorer is working to some extent. However, if it’s frozen, you’ll have to go through Settings.
Step 4: Open Settings (Win key + I) and search for ‘File Explorer Options’. This will open a small window.
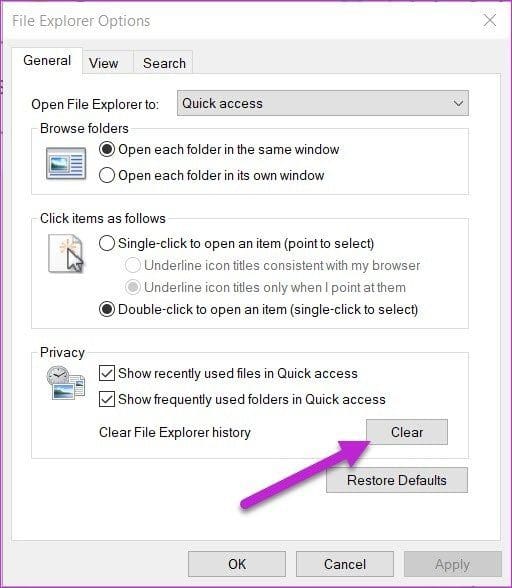
Now, click on the Clear button under Privacy to clear the Windows Explorer history.
6. Run Disk Clean-up
If the above fixes have failed to run Windows Explorer, you might want to run Disk Clean-up. As suggestive of its name, it gets rid of temporary files and folders that litter your PC.
Step 1: Search for Disk Clean-up. Select C: drive from the menu.
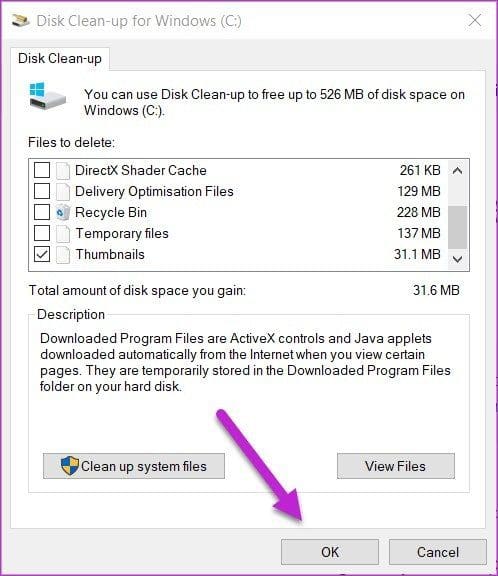
Step 2: Once the Disk Clean-up window is open, check the options for Downloaded Program Files, Temporary Internet Files, and Thumbnails from the list, and click on OK.
7. Rebuild the Index
Another possible reason for the Explorer not responding or acting slowly may be a slow indexing service. If the File Explorer is slow to load results (or crashes unexpectedly), it’s time you rebuilt the index.
Step 1: Search for the Indexing Option on the Search menu.
Step 2: Once you locate it, click on the Advanced button at the bottom. Now, under Troubleshooting, click on the Rebuild button.
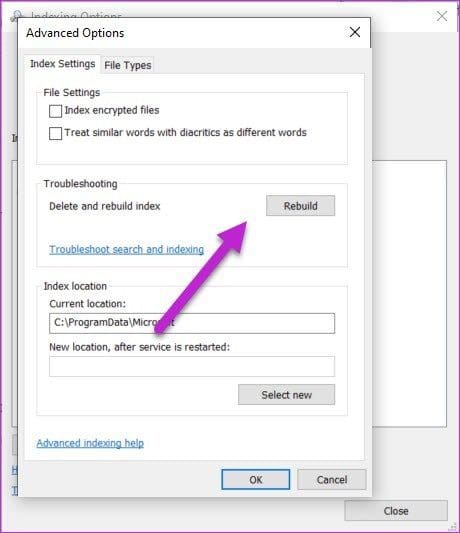
If the issue with File Explorer not responding is tied to the file indexing, the above should fix your issue. Then, restart your PC.
8. Launch in a Separate Process
Even if you have managed to repair the issue with Windows Explorer, the odds are that it might occur again. Hence, it’s best to force the File Explorer window to run in a separate process.
While Windows claims that it’s set by default on most Windows 10 systems, however, it doesn’t hurt to take a second look.
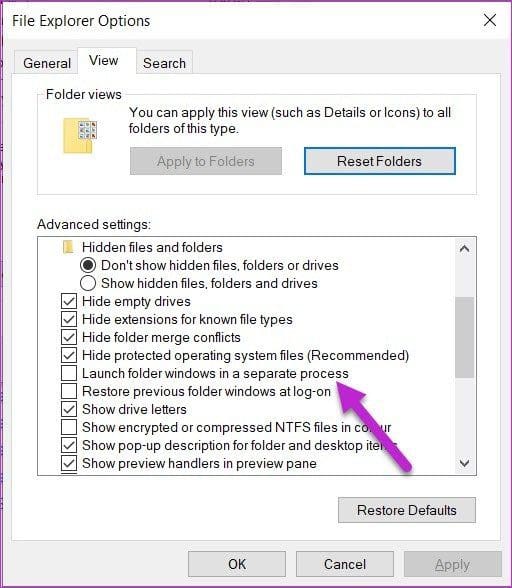
Search for File Explorer Options in the start menu. After you locate it, select View. Next, check the option for Launch folder windows in a separate process.
If it’s unchecked, check it and tap on OK to save your changes.
9. Check for Corrupt Files
The veteran Windows user in you must know how corrupted files can wreck up the system. If some core Windows files had failed to update during past updates, it could cause the Explorer to malfunction.
Again, there’s a way to fix some corrupted files by running the built-in System File Checker (SFC). As you may have guessed, SFC checks the system for corrupted files or missing files and restores them automatically.
Note: However, running the SFC should only be seen as one of the last remaining solutions since it can be risky. We recommend you take a backup of your PC before proceeding with it.
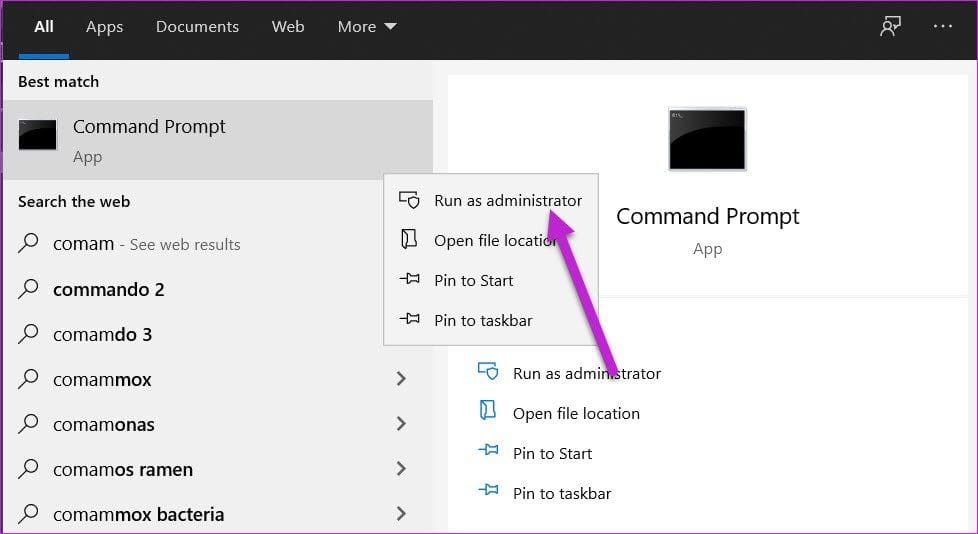
Step 1: Launch the Start menu and search for Command Prompt. Right-click and select Run as Administrator.
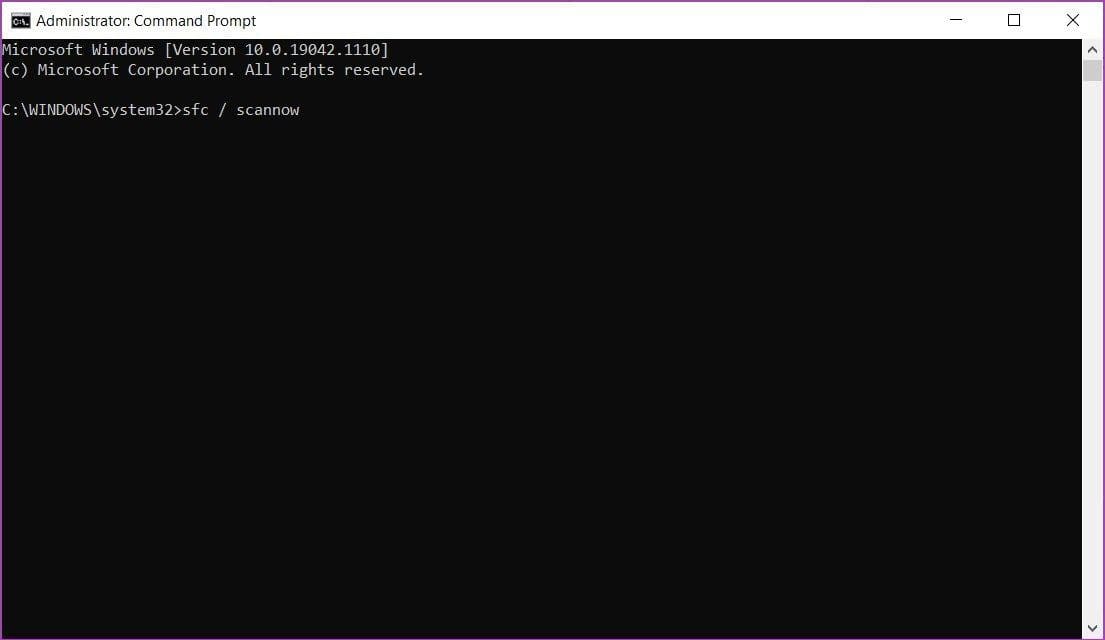
Step 2: Once the Command Prompt window opens, type the following command.
sfc /scannow
Naturally, this will take some time. Once the command has finished executing, you will do something along the lines of ‘…found corrupt files and successfully repaired them…’.
Restart your PC, and the good old Windows File Explorer should be back in action.
That is everything you need to know about what to do if File Explorer is not responding on your Windows PC. If you have any further questions, you can take a look at the FAQ section below.
FAQs: Windows Explorer Not Responding
The Windows Explorer process is likely shutdown. Use ‘Ctrl + Alt + Del’ to open the task manager. Select ‘Run New Task’ and enter ‘explorer.exe’.
You can restart the Windows Explorer process as shown in one of the methods above. If not try restarting your PC.
Fix Unresponsive File Explorer on Windows
We hope this article helps you fix the issue with the File Explorer. At the end of the day, your system needs to have enough disk space and RAM to run all the processes seamlessly, especially Windows Explorer. If it’s so, the above can only temporarily fix the issues.
Was this helpful?
Last updated on 28 December, 2023
The article above may contain affiliate links which help support Guiding Tech. The content remains unbiased and authentic and will never affect our editorial integrity.